Prisma SD-WAN
Configure IPSec and GRE in Prisma SD-WAN
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma SD-WAN Docs
-
-
- Prisma SD-WAN Controller
-
- CloudBlade Integrations
- CloudBlades Integration with Prisma Access
-
-
-
-
- 6.5
- 6.4
- 6.3
- 6.1
- 5.6
- Prisma SD-WAN Controller
- Prisma SD-WAN On-Premises Controller
- Prisma SD-WAN CloudBlades
- Prisma Access CloudBlade Cloud Managed
- Prisma Access CloudBlade Panorama Managed
Configure IPSec and GRE in Prisma SD-WAN
Lets see how to configure IPSec and GRE tunnel configuration in the Prisma SD-WAN web interface.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
This workflow simplifies the integration between Prisma SD-WAN and Zscaler by
automating the creation, management, and maintenance of third-party IPSec VPN
tunnels. By leveraging this one-touch integration, branch sites can seamlessly
connect to Zscaler without manual configuration.
After the CloudBlade is configured, the next task is to configure Prisma SD-WAN
sites, and tag the circuit categories to denote which sites and circuit types are
candidates for auto Standard VPN tunnel and GRE tunnel creation to Zscaler.
- In Strata Cloud Manager, go to ConfigurationPrisma SD-WANBranch Sites.Switch to List View, search for the required branch site, and open the site details page.
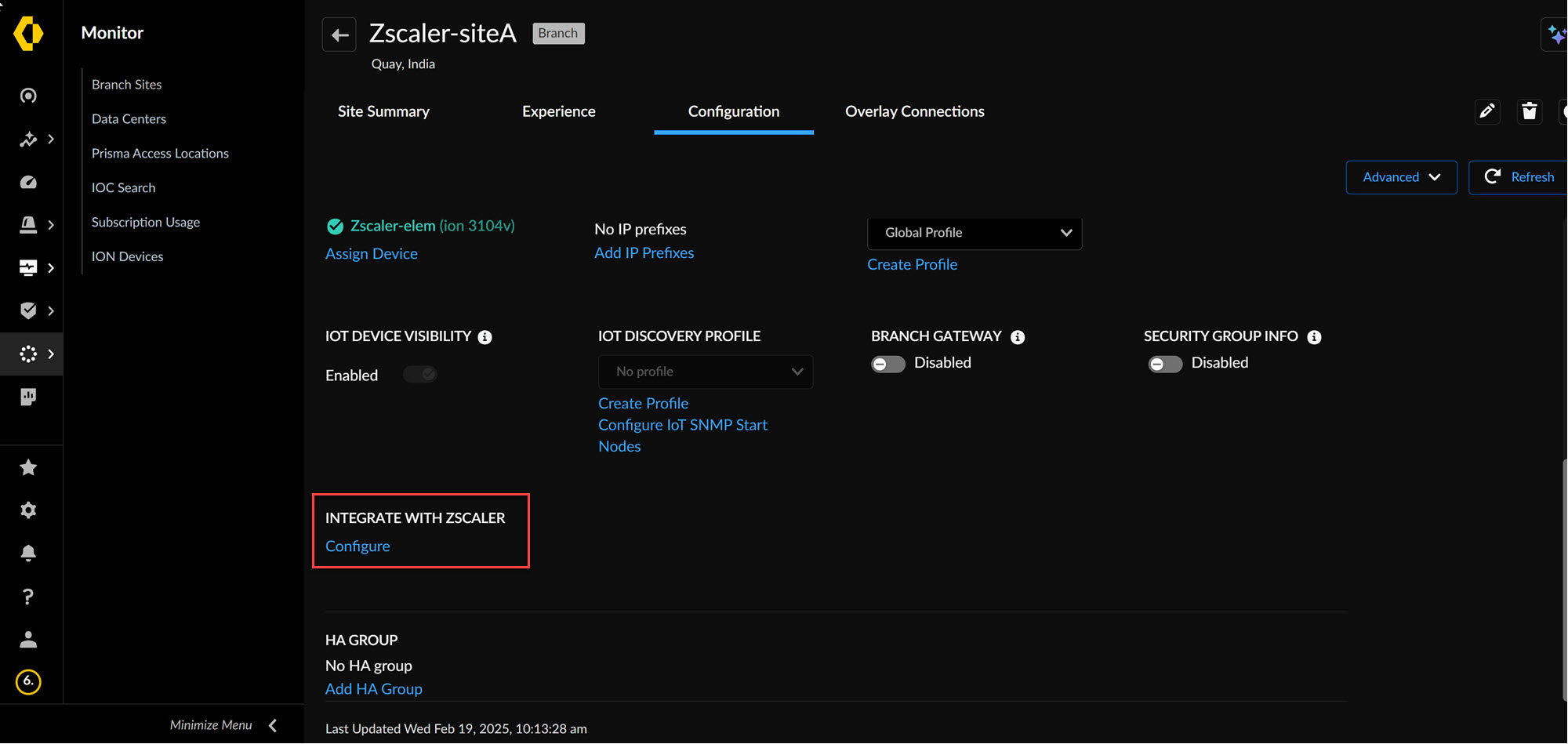
![]() Go to the Configurations tab and click Configure to initiate the Zscaler integration process.
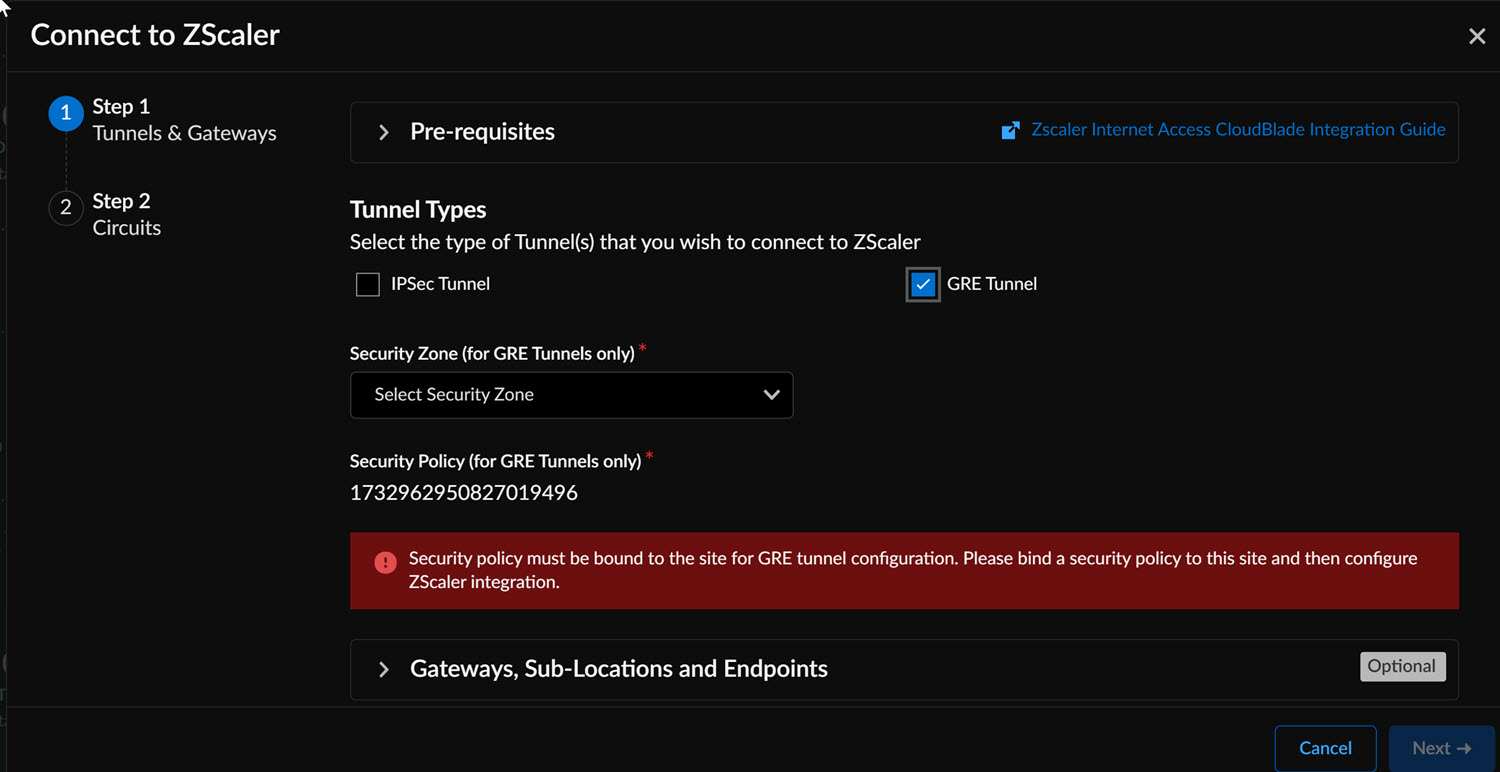
Go to the Configurations tab and click Configure to initiate the Zscaler integration process.![]() The Configure button remains disabled if no circuits are attached or the CloudBlade is not enabled.On the Connect to Zscaler screen, select the tunnel type (IPSec or GRE) for configuration.To configure the GRE Tunnel, ensure that a Security Zone is associated with a Security Policy, and the Security Policy is bound to the site. Associating a Security Zone is mandatory for GRE tunnels. Go here to configure GRE endpoints for both primary and secondary tunnels.Select the preconfigured Security Zone and specify the Custom Endpoint for both primary and secondary tunnels (version 2.0.0 onwards).
The Configure button remains disabled if no circuits are attached or the CloudBlade is not enabled.On the Connect to Zscaler screen, select the tunnel type (IPSec or GRE) for configuration.To configure the GRE Tunnel, ensure that a Security Zone is associated with a Security Policy, and the Security Policy is bound to the site. Associating a Security Zone is mandatory for GRE tunnels. Go here to configure GRE endpoints for both primary and secondary tunnels.Select the preconfigured Security Zone and specify the Custom Endpoint for both primary and secondary tunnels (version 2.0.0 onwards).![]() When using custom endpoints for GRE tunnels, ensure the IP addresses are listed among the closest data centers and belong to data centers in different locations.To configure the IPSec tunnel, set up a custom Standard VPN Endpoint if needed instead of the one managed by CloudBlade.Configure the Gateway, Sub-Locations, and Endpoints options.
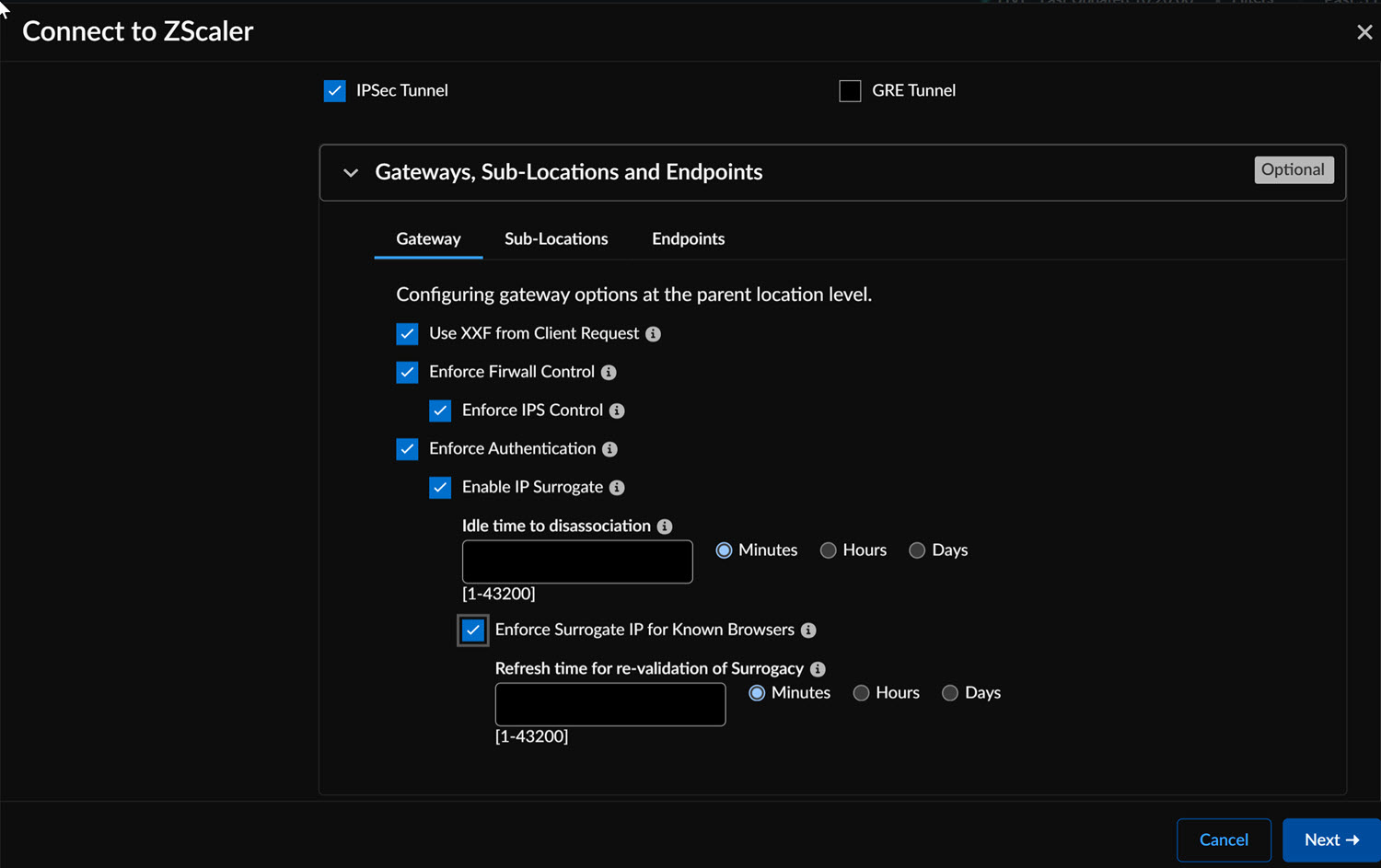
When using custom endpoints for GRE tunnels, ensure the IP addresses are listed among the closest data centers and belong to data centers in different locations.To configure the IPSec tunnel, set up a custom Standard VPN Endpoint if needed instead of the one managed by CloudBlade.Configure the Gateway, Sub-Locations, and Endpoints options.- To configure the Gateway options at the parent
location level, select the required settings to ensure all traffic from
this location follows the configured options.
![]()
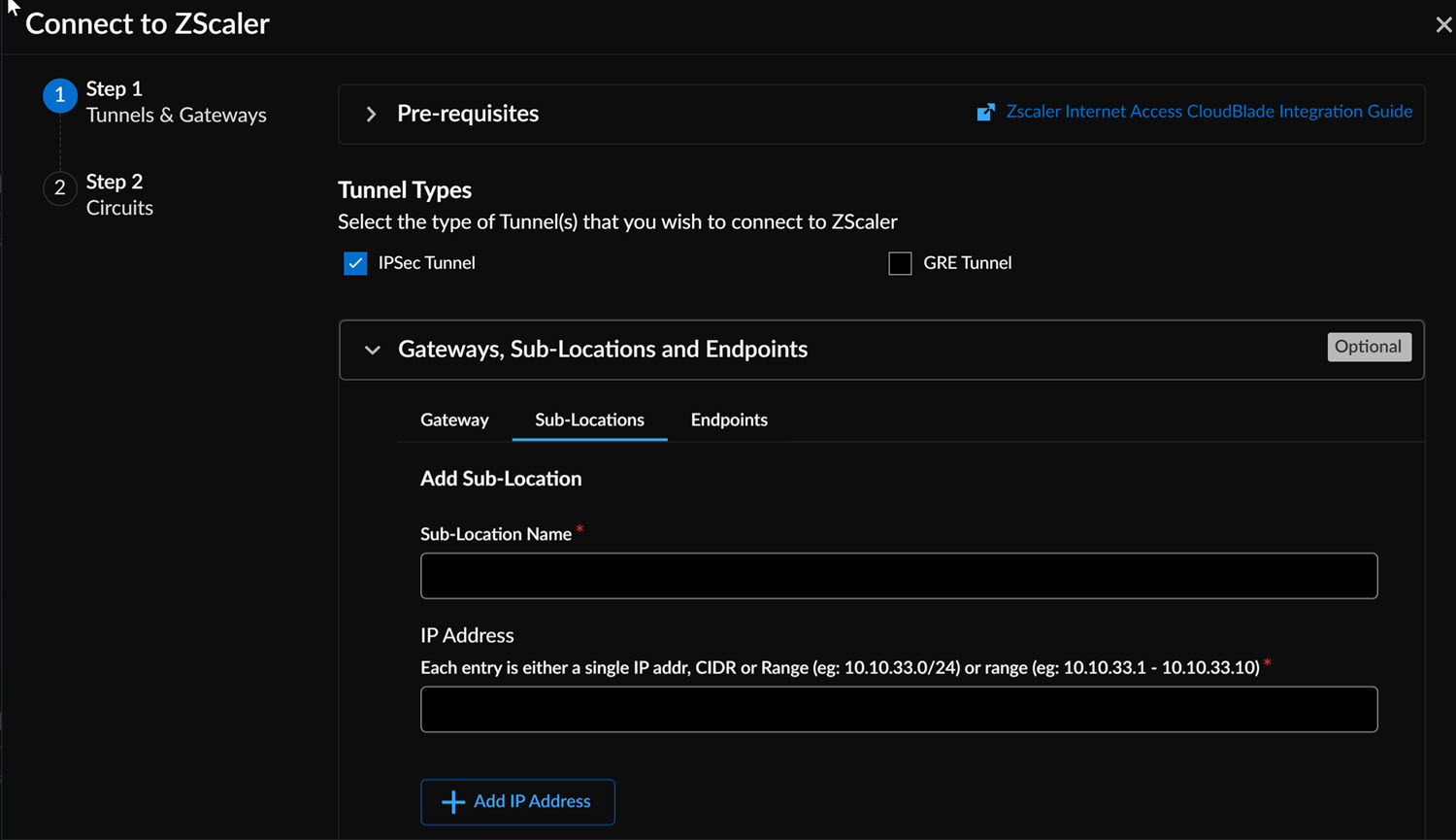
- To configure different gateway option settings for different sources of
traffic from this site, define sub-locations by entering the
sub-location name and IP address under the
Sub-Locations tab.
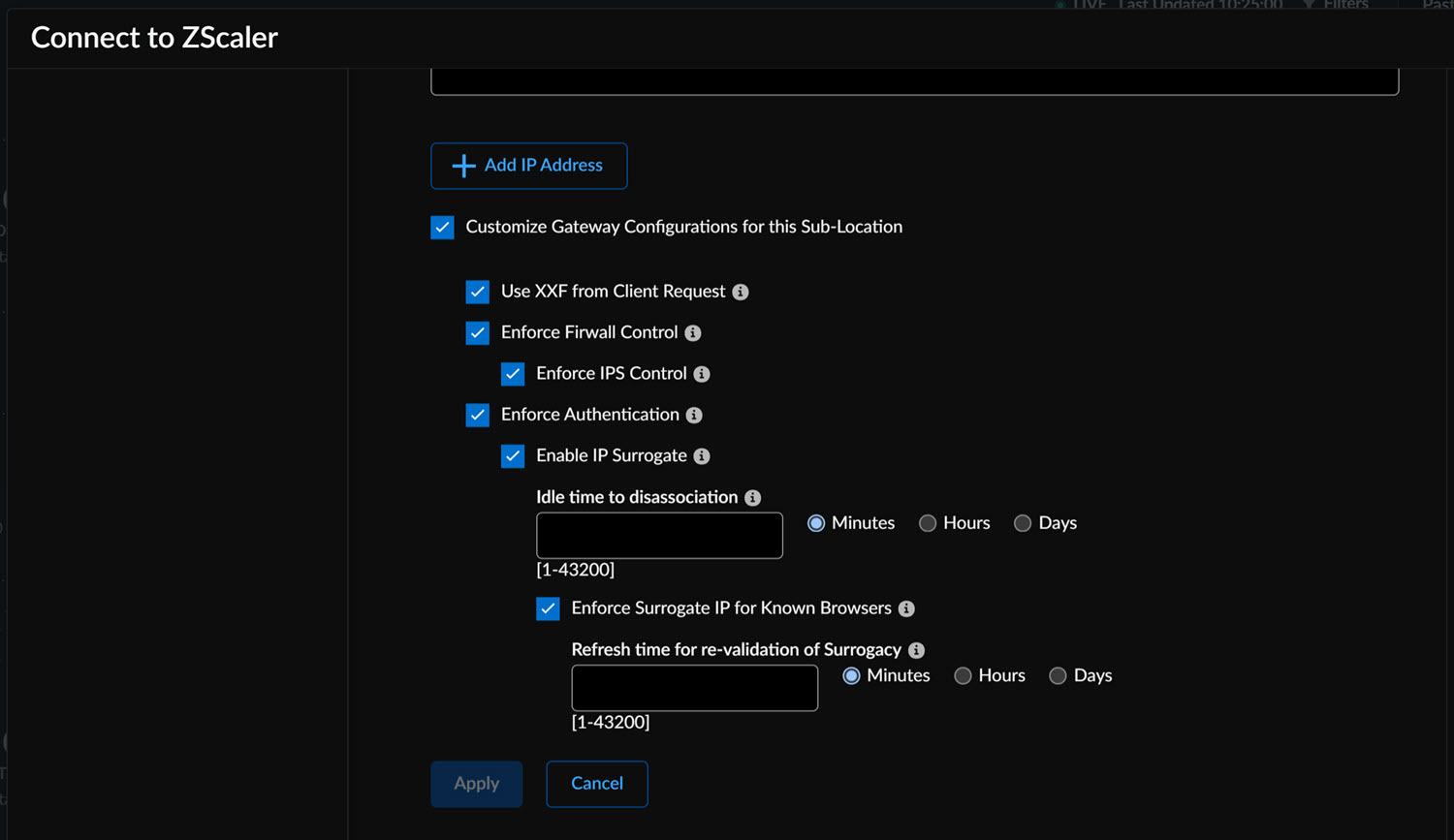
![]() You can enter multiple IP addresses for the sub-location. Each sub-location entry can be a single IP address, CIDR, or range.Adding the first sub-location automatically creates a new sub-location called Other. All existing policy rules that reference the parent location will now apply to the other location. You must manually configure rules for traffic from this sub-location.You can enable the following options in Gateways or Sub-Locations to customize configurations.
You can enter multiple IP addresses for the sub-location. Each sub-location entry can be a single IP address, CIDR, or range.Adding the first sub-location automatically creates a new sub-location called Other. All existing policy rules that reference the parent location will now apply to the other location. You must manually configure rules for traffic from this sub-location.You can enable the following options in Gateways or Sub-Locations to customize configurations.![]()
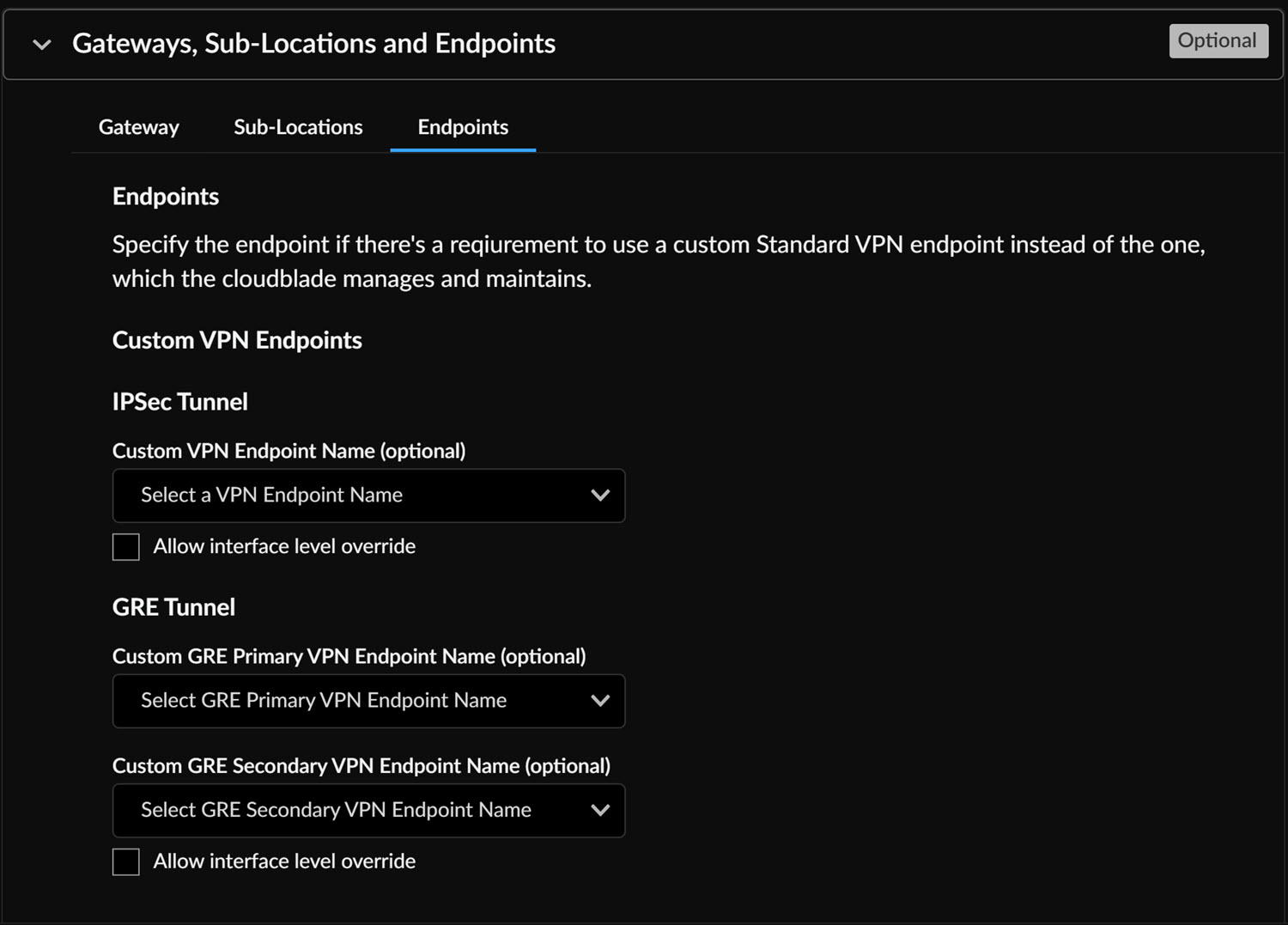
Gateway Option Description Enable XFF from Client Request Use this option if the location employs proxy chaining to forward traffic to the service and you want Zscaler to utilize X-Forwarded-For (XFF) headers inserted by your on-premise proxy. When forwarding traffic to its destination, Zscaler removes the original XFF header and replaces it with the IP address of the client gateway (public IP) to prevent exposure of internal IP addresses. Enforce Firewall Control Activates the firewall at the specified location. Enforce IPS Control Enables user-to-device mapping when an internal IP can be differentiated from a public IP. This ensures user policies apply to cookie-incompatible traffic. Enforce Authentication Requires identification of individual user traffic using the configured authentication mechanism. Enforce Caution Enforces a caution policy action by displaying an end-user notification for unauthenticated traffic. If disabled, the action is treated as Allow. Enforce AUP(Acceptable Use Policy) Displays an Acceptable Use Policy (AUP) for unauthenticated traffic and requires users to accept it. Enforce IP Surrogate Enables user-to-device mapping for enforcing user policies when an internal IP can be distinguished from a public IP. This is essential for cookie-incompatible traffic. Idle Time to Disassociation If IP Surrogate is enabled, specifies the duration after a completed transaction before the service removes the IP-to-user mapping. Enforce Surrogate IP for Known Browsers If enabled, surrogate user identity is used for traffic from known browsers if an IP-user mapping exists. If disabled, traffic from known browsers will always be authenticated using the configured authentication mechanism. Surrogate Identity Refresh Interval Defines how long a surrogate user identity can be used before requiring revalidation via authentication. The refresh interval must be shorter than the DHCP lease time to prevent incorrect user policies from being applied. Custom AUP Frequency Specifies, in days, how often the Acceptable Use Policy is displayed to users. Block Internet Access Disables all internet access, including non-HTTP traffic, until the user accepts the Acceptable Use Policy. By default, any changes to the IPSec and GRE configurations apply automatically to both the gateway and sub-locations. - Specify the Endpoints from the drop-down if you
need to use Custom VPN Endpoints for IPSec
tunnels and GRE tunnels (primary and secondary) instead of those managed
by the CloudBlade. If using a custom endpoint, enter the preconfigured Standard VPN Endpoint name (case-sensitive) to be referenced when the CloudBlade configures the Standard VPN interfaces at this site. If no endpoint is specified, the CloudBlade will default to using the ZScaler Standard VPN endpoint, which includes a list of all ZEN node hostnames.
![]() If required, enable Interface level override for further customization.
If required, enable Interface level override for further customization.
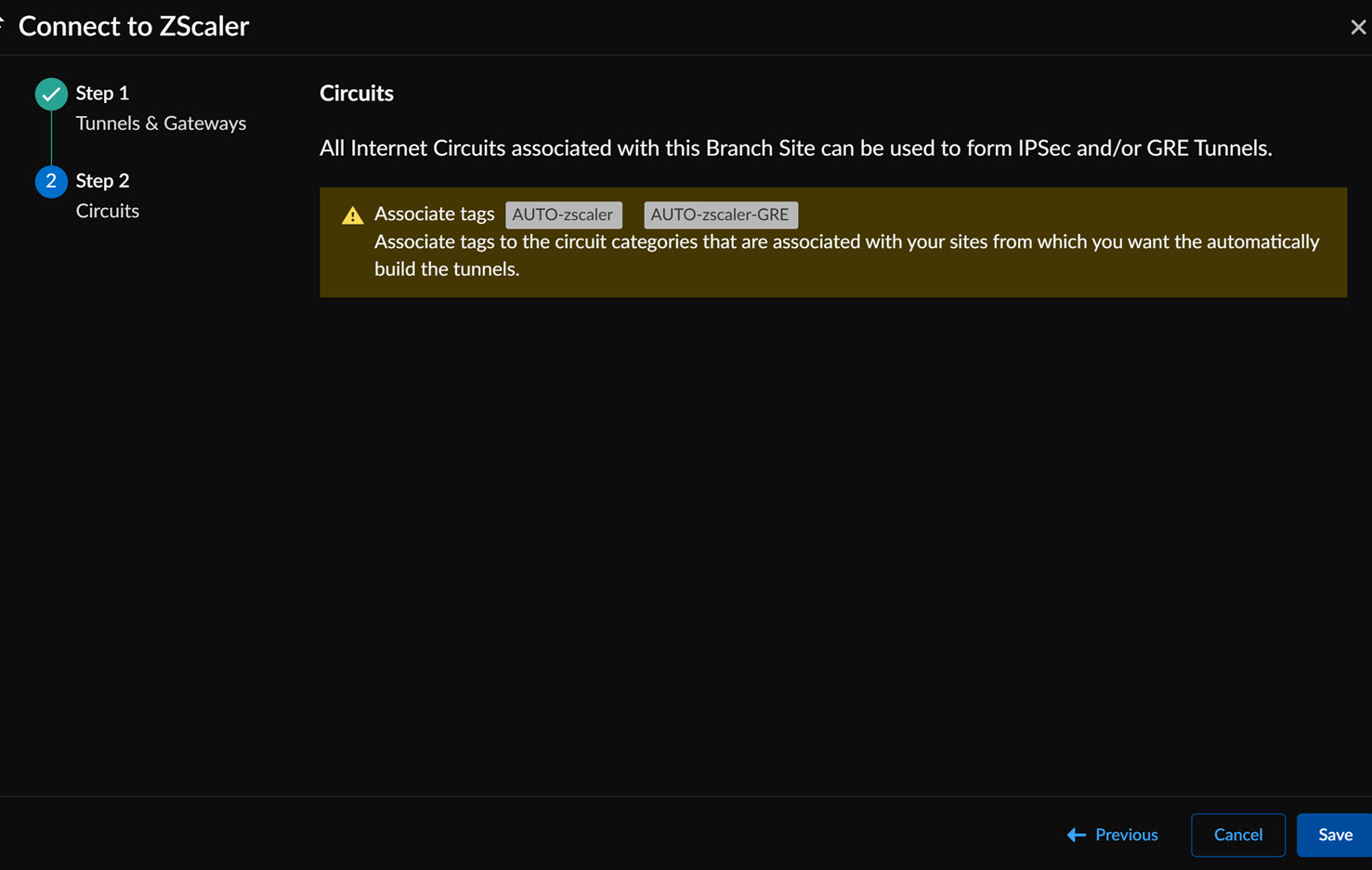
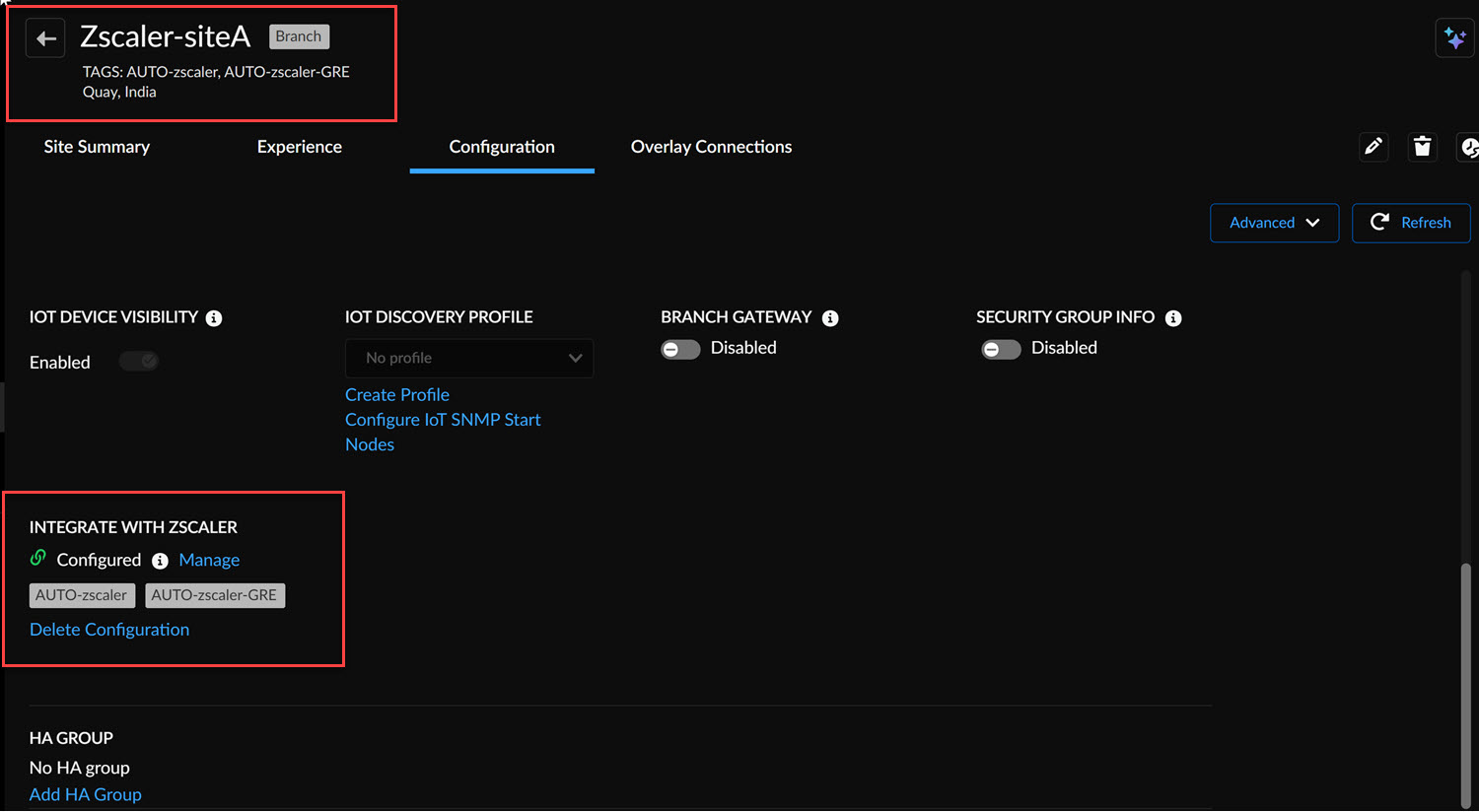
Tag the circuit categories.![]() Once the site is enabled for Zscaler, all Internet Circuits associated with this Branch Site can be used to form IPSec and/or GRE Tunnels. The IPSec and GRE configurations will be associated with the circuit categories to allow automatic tunnel formation.You can validate the tunnel configuration by navigating to the Branch Site and confirming if the tags are configured correctly.
Once the site is enabled for Zscaler, all Internet Circuits associated with this Branch Site can be used to form IPSec and/or GRE Tunnels. The IPSec and GRE configurations will be associated with the circuit categories to allow automatic tunnel formation.You can validate the tunnel configuration by navigating to the Branch Site and confirming if the tags are configured correctly.![]()
- Select Delete Configuration (if required), and select the tunnel type (IPSec or GRE) to remove the Zscaler configuration from the branch site.
- Select Manage to edit any of the existing IPSec and GRE configurations.
Tag the Circuit Categories
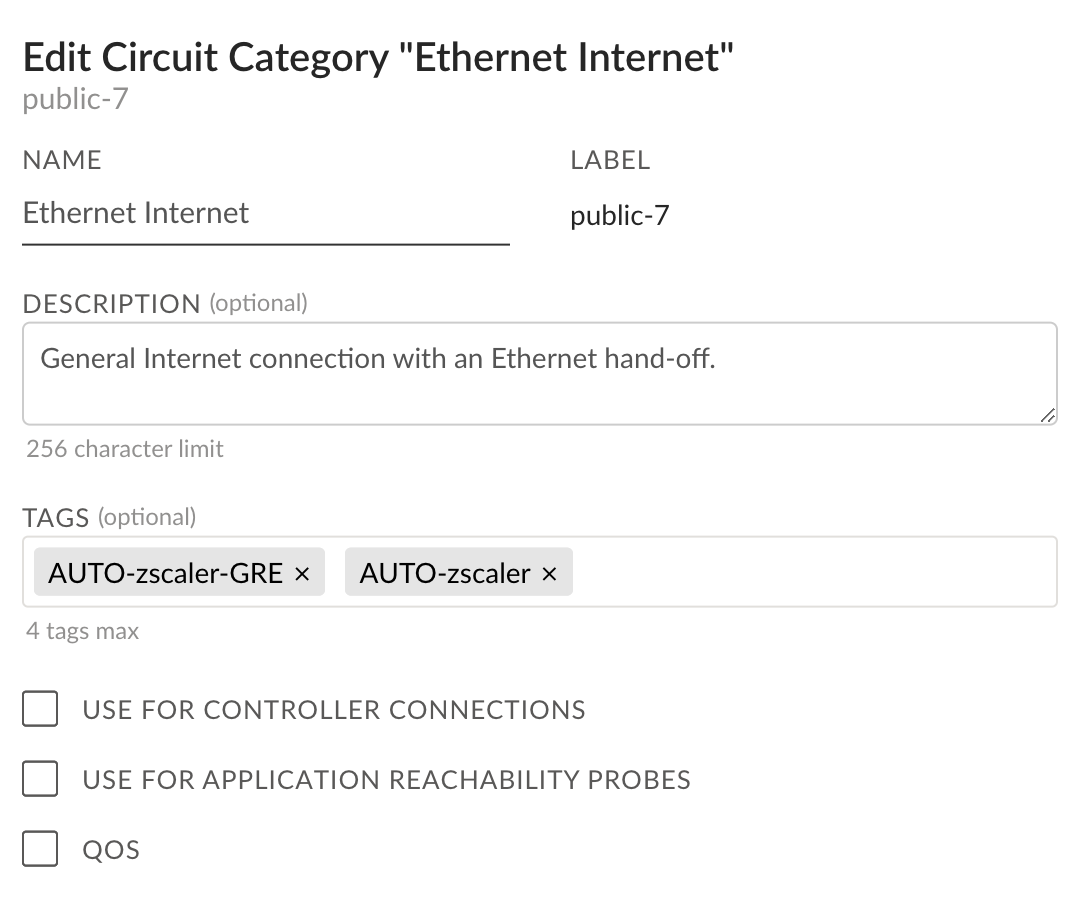
Now that the site has been tagged as enabled for Zscaler, we need to tag the circuit categories that can be used to establish a Standard VPN or GRE tunnel to Zscaler.This capability is useful if you want only specific types of circuits to be used for Zscaler integration or explicitly exclude certain circuit types. For example, a customer may not want to use their metered LTE circuit for Standard VPN establishment.- In Strata Cloud Manager, go to ConfigurationPrisma SD-WANResourcesCircuit Categories.Find the circuit categories that are associated with your sites from which you want the system to automatically build the tunnels. Edit the circuit category, and enter AUTO-zscaler and AUTO-zscaler-GRE (case sensitive) in the Tags field.
![]() Select Update.Once this configuration is completed, Standard VPN IPsec/GRE tunnels connecting the Prisma SD-WAN ION device and Zscaler will begin the creation or onboarding process in the next integration cycle. It may take several integration cycles for the tunnels to appear and be active on the Prisma SD-WAN portal.
Select Update.Once this configuration is completed, Standard VPN IPsec/GRE tunnels connecting the Prisma SD-WAN ION device and Zscaler will begin the creation or onboarding process in the next integration cycle. It may take several integration cycles for the tunnels to appear and be active on the Prisma SD-WAN portal.