SaaS Security
Begin Scanning a Google Drive App
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
SaaS Security Docs
Begin Scanning a Google Drive App
Add your Google Drive app to Data Security to begin scanning and monitoring
assets for possible security risks.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
Or any of the following licenses that include the Data Security license:
|
Data Security supports both My Drive and Shared Drives. Files in My Drive are
individually owned whereas files in Shared Drives belong to members of a team.
Groups in a team are not supported.
Ensure that the Super Admin account
added to the Strata Cloud Manager for onboarding Google Drive app has logged in at
least once into the Strata Cloud Manager. Only then will the account be enabled.
Onboarding will fail if this account has never logged into the Strata Cloud Manager.
Support for automated remediation
capabilities varies by SaaS application.
- Supported Content
- Onboard Google Drive App
- Troubleshooting Onboarding for Google Drive App
- Selective Scanning on Google Drive App
- Start Scanning and Monitor Results
- Google Drive App Behaviors
- Create Domain Wide Delegation
Whether files are individually owned and shared (My Drive) or belong to members in a
team (Shared Drives), Data Security scans and protects the assets because your
end users can share data externally from Shared Drives as easily as they can from My
Drive.
Supported Content
|
Support For
|
Details
|
|---|---|
|
Scan Content
| Files, Folders |
|
Backward Scan
|
Yes
|
|
Forward Scan
|
Yes
|
|
Rescan
|
Yes
|
|
Selective Scan
|
Yes
|
|
Exposure
|
All
|
|
Remediation Actions
|
My Drive
Shared Drives
|
|
Post-Remediation Actions (Actions after Admin
Quarantine):
You can delete, restore, or download a quarantined file
after performing a remediation action (for example
quarantine or incident generation).
|
When a file is restored from Admin Quarantine,
collaborators are not restored.
|
|
Notifications
|
|
|
User Activities
|
|
|
Snippet Support
|
Yes
|
|
Known License and Version restrictions
|
Supported Versions
|
|
Caveats and Notes
|
None
|
Onboard Google Drive App
Google’s default Super admin role provides the necessary communication between
Data Security and the Google Drive app. This Super admin role:
- Can read, write, and relocate assets in the app.
- Has API access. API access provides visibility into the assets in Google Drive and enables Data Security to monitor the sharing of assets.
- Prerequisites to be completed on Google Drive
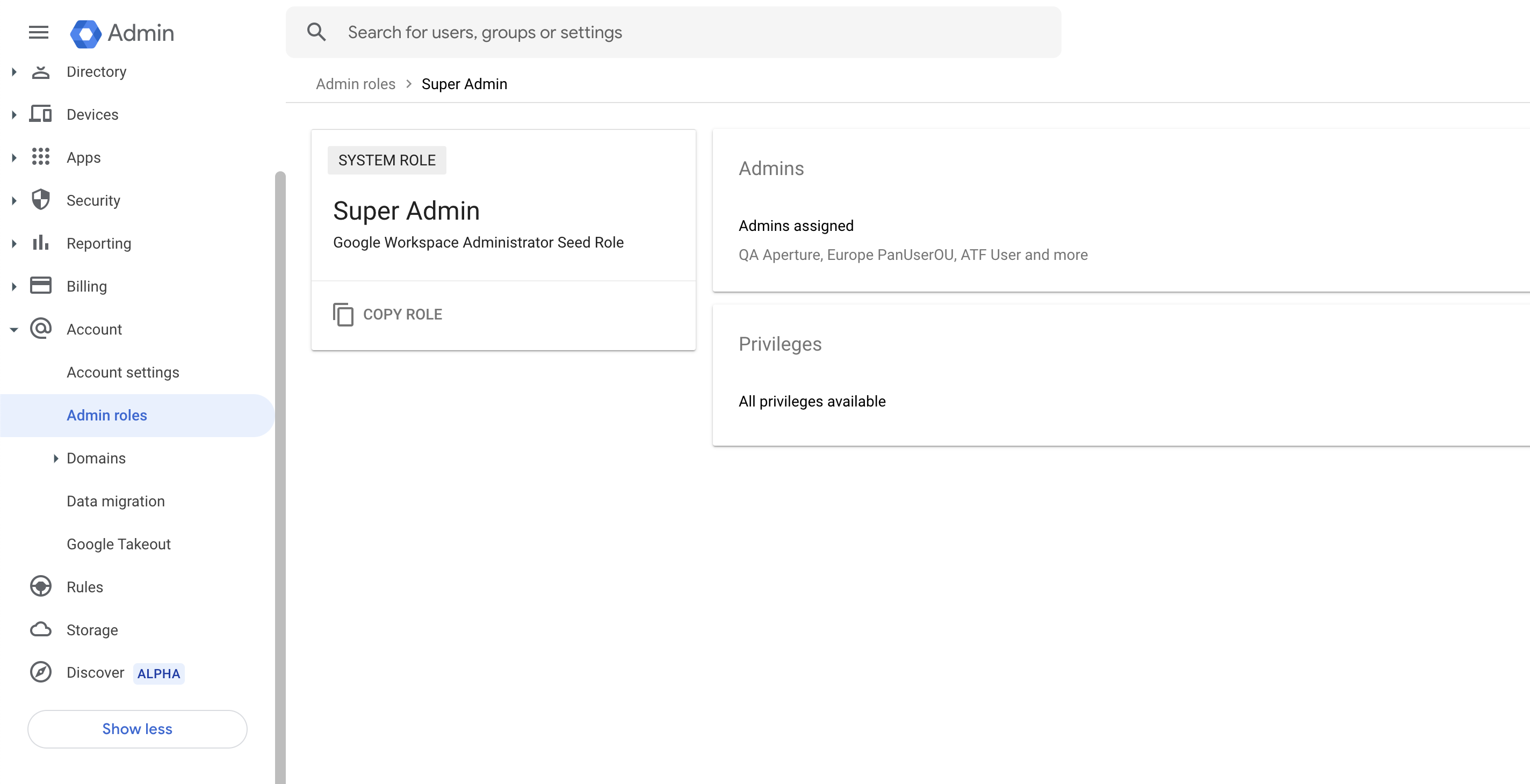
- Verify that your Google Drive administrator account is assigned Super admin role.
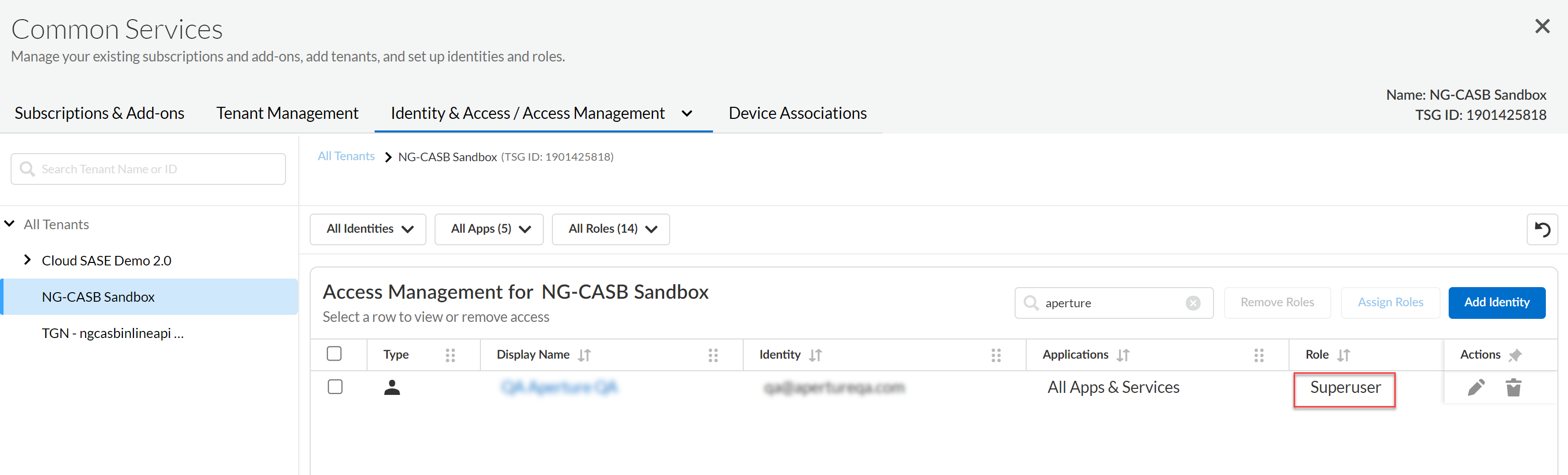
![]() Ensure that the Google Drive administrator account’s domain matches the existing domain on Data Security.(Recommended) Add your Google Drive domain as an internal domain.Log in to Google Marketplace using an account with Super admin role permissions. To do this, go to Google Workspace Marketplace and first log out of Google Marketplace to ensure that you're not logged in as a user other than an account with Super admin role permissions. Then log in with an account that has Super admin permissions.Add the same email address of the Google Drive administrator to Data Security and assign a Superuser role.
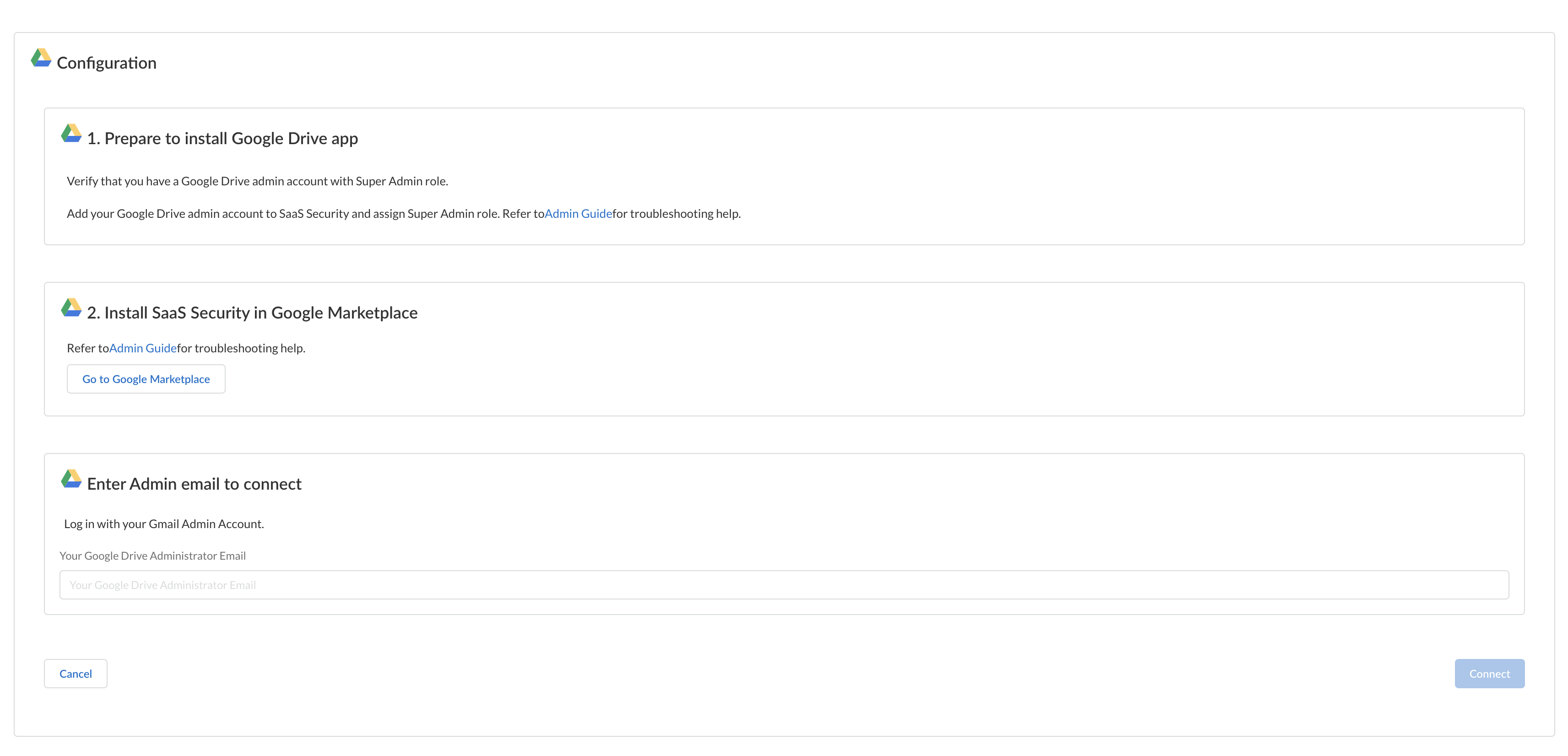
Ensure that the Google Drive administrator account’s domain matches the existing domain on Data Security.(Recommended) Add your Google Drive domain as an internal domain.Log in to Google Marketplace using an account with Super admin role permissions. To do this, go to Google Workspace Marketplace and first log out of Google Marketplace to ensure that you're not logged in as a user other than an account with Super admin role permissions. Then log in with an account that has Super admin permissions.Add the same email address of the Google Drive administrator to Data Security and assign a Superuser role.![]() Next step: Add Google Drive App to Data Security.Add Google Drive App to Data Security
Next step: Add Google Drive App to Data Security.Add Google Drive App to Data Security- To add the Google Drive app, log in to Strata Cloud Manager and select ConfigurationData SecurityApplicationsAdd ApplicationGoogle Drive .
![]()
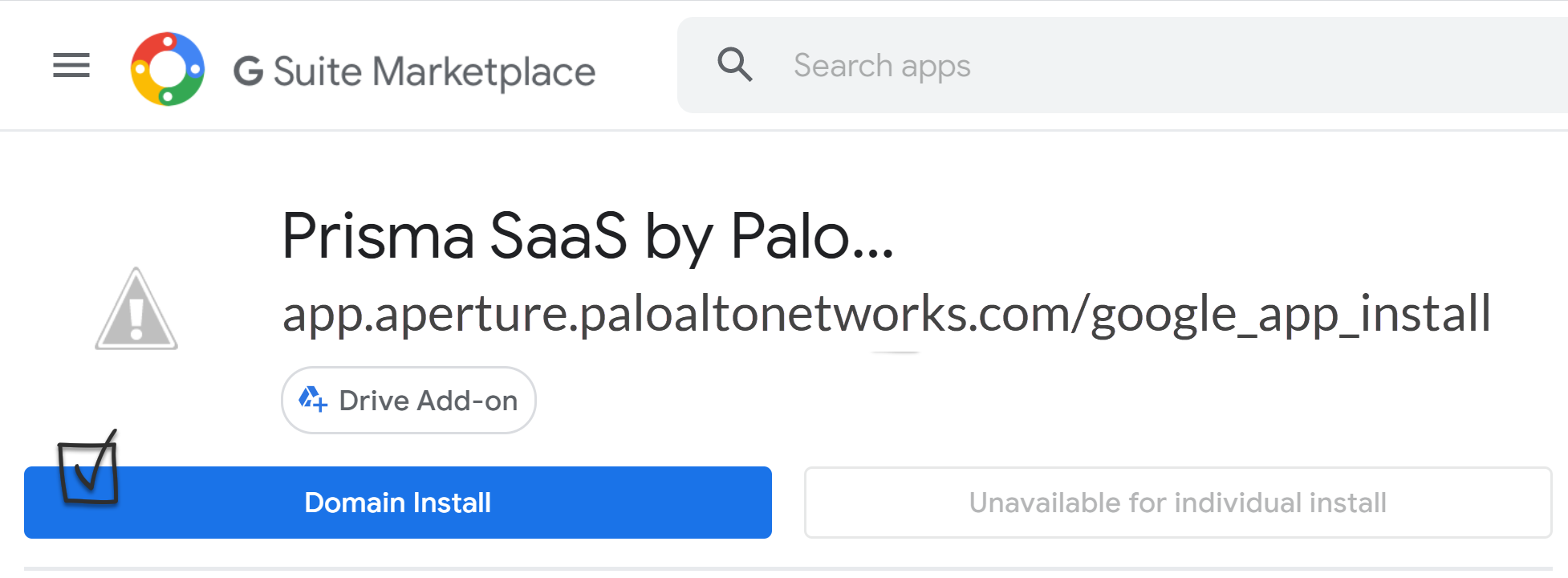
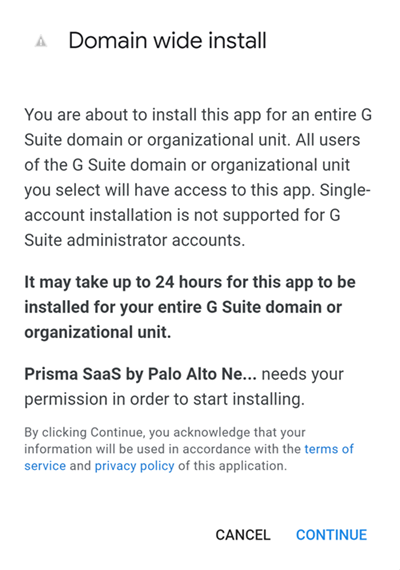
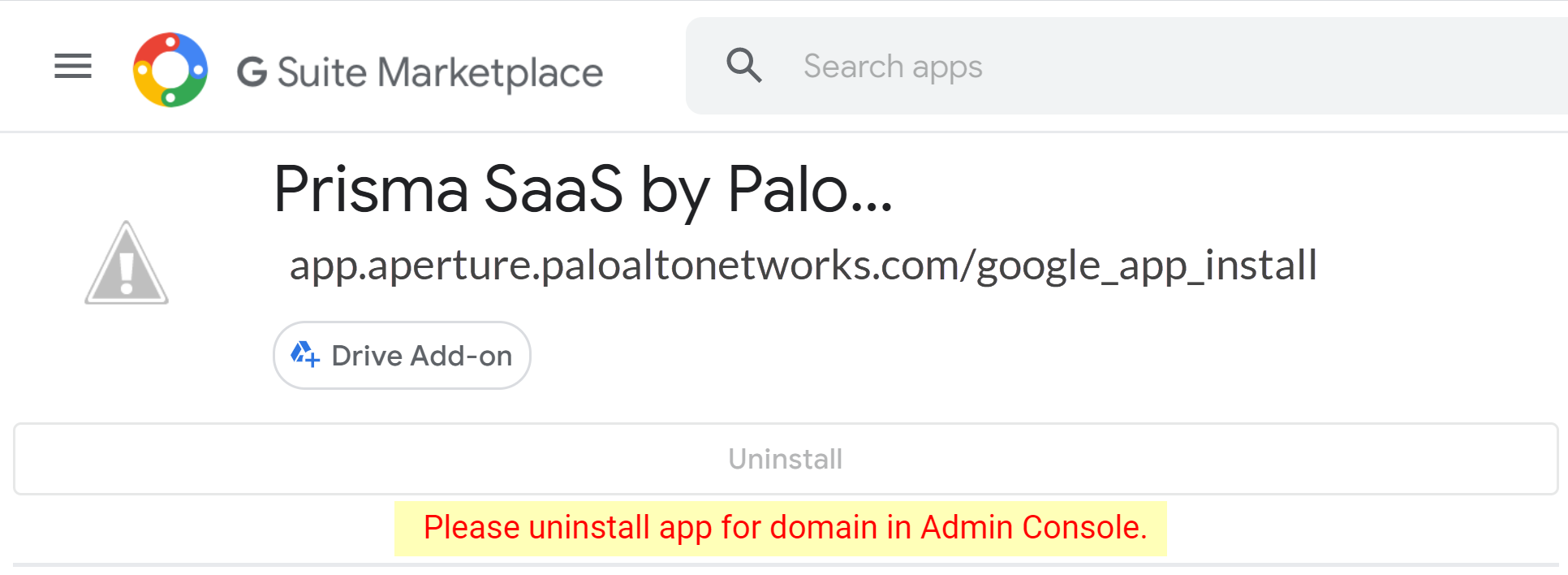
![]() Before you begin: As indicated in the onscreen instruction 1, ensure that you complete the prerequisites.To onboard your Google Drive app, use Domain wide delegation and skip to Sub Step 9 (Connect to Google Drive Account) OR perform the following Sub Steps 4 to 8.Follow the onscreen instruction 2: Go to Google Marketplace. Afterward, the Domain Install button is replaced by a disabled Uninstall button with a message that reads Please uninstall app for domain in Admin Console. This behavior is expected.Select Domain Install on the Google Marketplace page.Don't go to the link provided. Doing so aborts the onboarding process. If you inadvertently click the redirect link, simply repeat the process starting with adding the Google Drive app to Data Security.
Before you begin: As indicated in the onscreen instruction 1, ensure that you complete the prerequisites.To onboard your Google Drive app, use Domain wide delegation and skip to Sub Step 9 (Connect to Google Drive Account) OR perform the following Sub Steps 4 to 8.Follow the onscreen instruction 2: Go to Google Marketplace. Afterward, the Domain Install button is replaced by a disabled Uninstall button with a message that reads Please uninstall app for domain in Admin Console. This behavior is expected.Select Domain Install on the Google Marketplace page.Don't go to the link provided. Doing so aborts the onboarding process. If you inadvertently click the redirect link, simply repeat the process starting with adding the Google Drive app to Data Security.![]() Click Continue to proceed with the Domain wide install process.
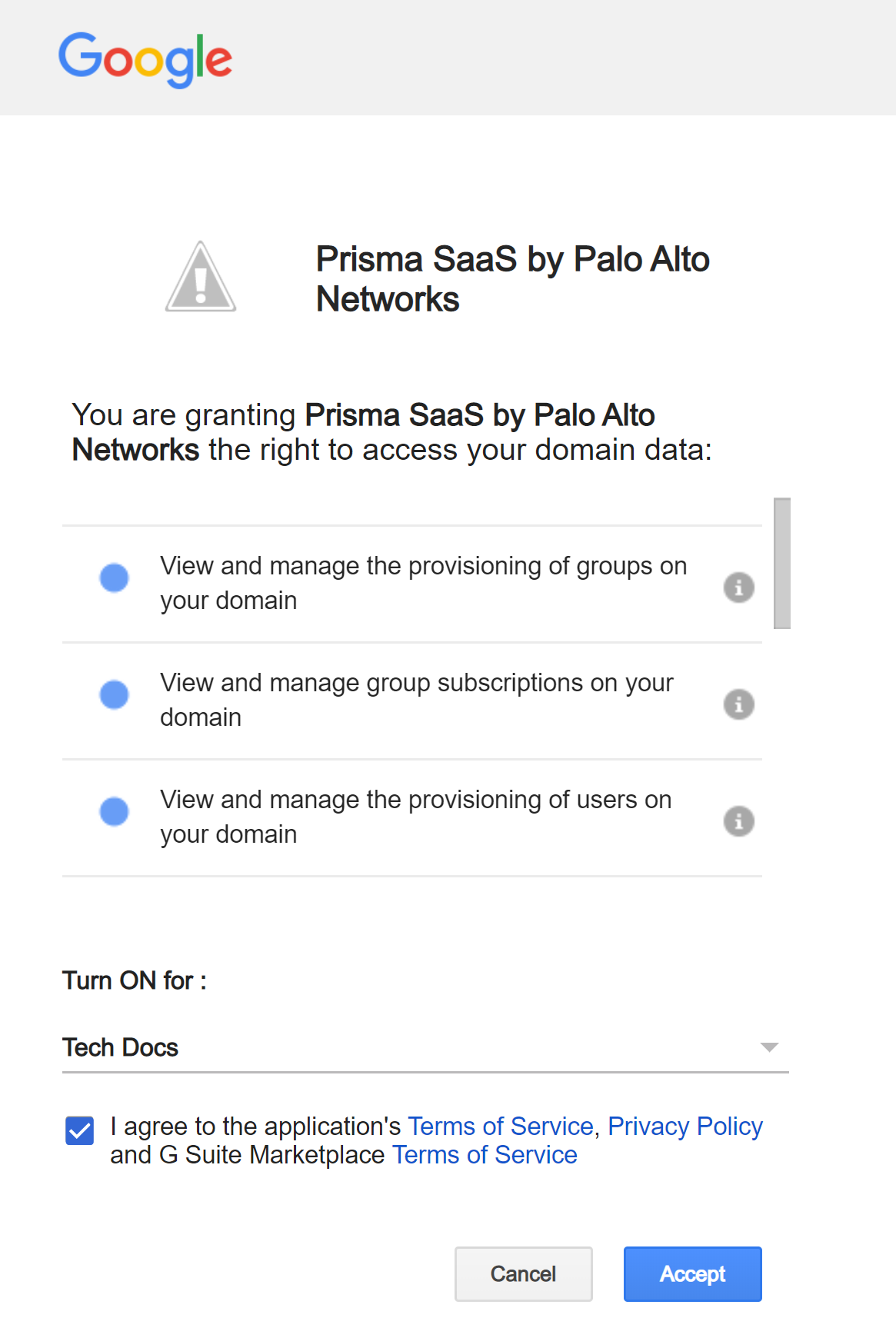
Click Continue to proceed with the Domain wide install process.![]() Review and Accept the requested permissions.Data Security requires these permissions to scan your assets on Google Drive. A new browser window opens in the foreground.
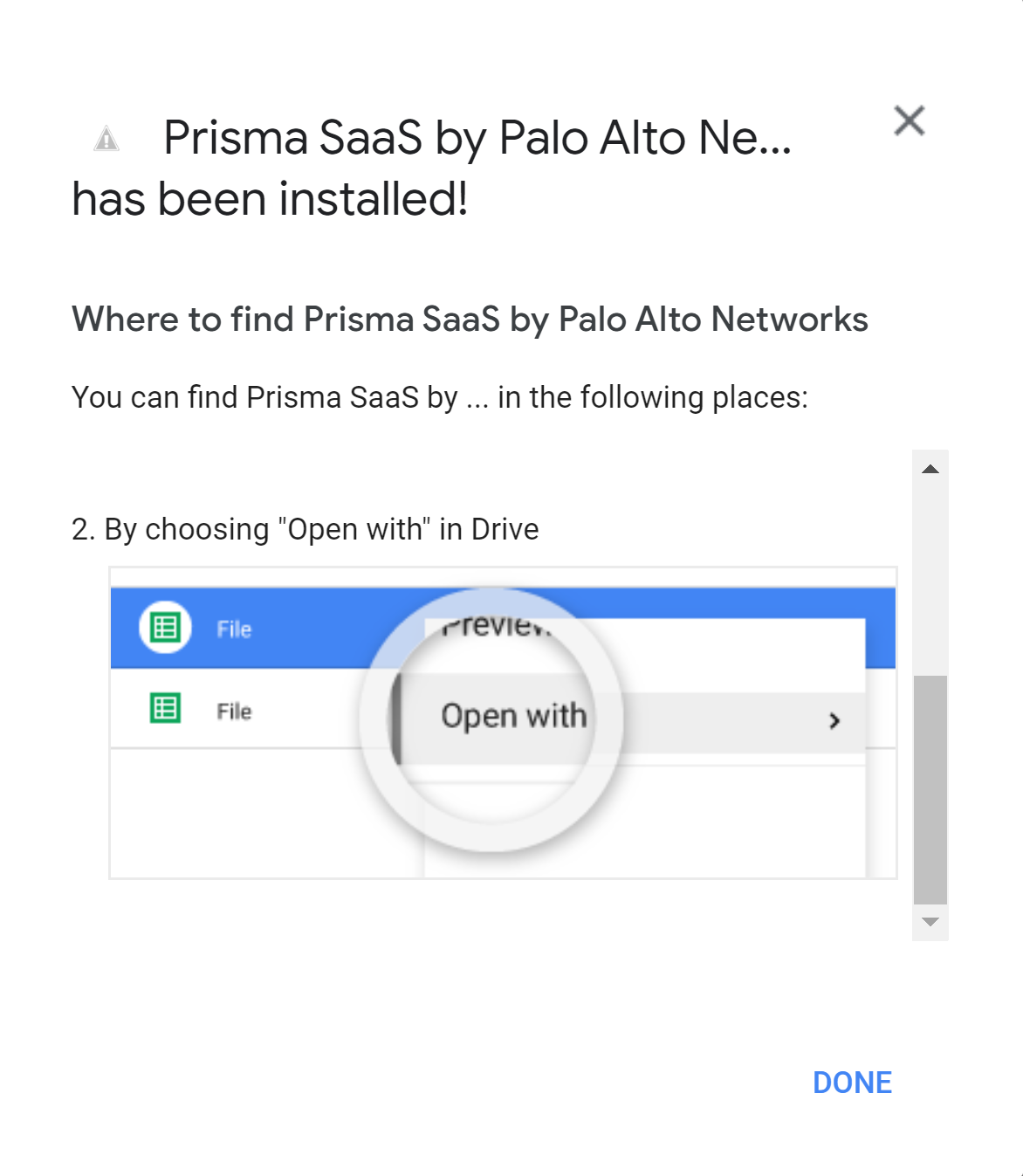
Review and Accept the requested permissions.Data Security requires these permissions to scan your assets on Google Drive. A new browser window opens in the foreground.![]() Click Done.
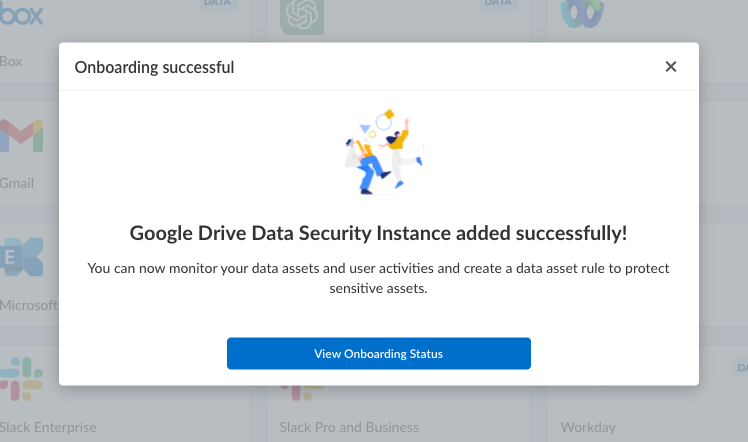
Click Done.![]() Follow the onscreen instruction 3: Connect to Google Drive Account.After you enter the Google Drive admin email, on successful onboarding, the following message is displayed.
Follow the onscreen instruction 3: Connect to Google Drive Account.After you enter the Google Drive admin email, on successful onboarding, the following message is displayed.![]() Click View Onboarding Status to know if the validation checks have passed. You will be able to start scanning only after successful validation.The Global administrator role is mandatory for the onboarding process. If you remove the Global Administrator role, Data Security will no longer be able to process any events or files.Optional Data Security adds the new Google Drive app to the Cloud Apps list as Google Drive n, where n is the number of Google Drive app instances that you connected to Data Security. For example, if you added one Google Drive app, the name displays as Google Drive 1 .Next step: Proceed to Selective Scanning on Google Drive App.
Click View Onboarding Status to know if the validation checks have passed. You will be able to start scanning only after successful validation.The Global administrator role is mandatory for the onboarding process. If you remove the Global Administrator role, Data Security will no longer be able to process any events or files.Optional Data Security adds the new Google Drive app to the Cloud Apps list as Google Drive n, where n is the number of Google Drive app instances that you connected to Data Security. For example, if you added one Google Drive app, the name displays as Google Drive 1 .Next step: Proceed to Selective Scanning on Google Drive App.Troubleshooting Onboarding for Google Drive App
The validation workflow is currently not available in FedRAMP Moderate. Instead, validation is confirmed by user activity.To ensure that your app has onboarded correctly without any issues in authentication or permissions, Data Security performs validation checks between the onboarding and scanning process. You can start scanning only after a successful validation. For Google Drive, the following three validations happen:- App Authentication
- User Permission
- Validating Permissions
After the validation is successful, Data Security displays the sample data assets and sample user activities.![]() If the App Authentication, User Permission, or Validating Permissions checks fail, try the following:
If the App Authentication, User Permission, or Validating Permissions checks fail, try the following:- Ensure you have administrator permissions.
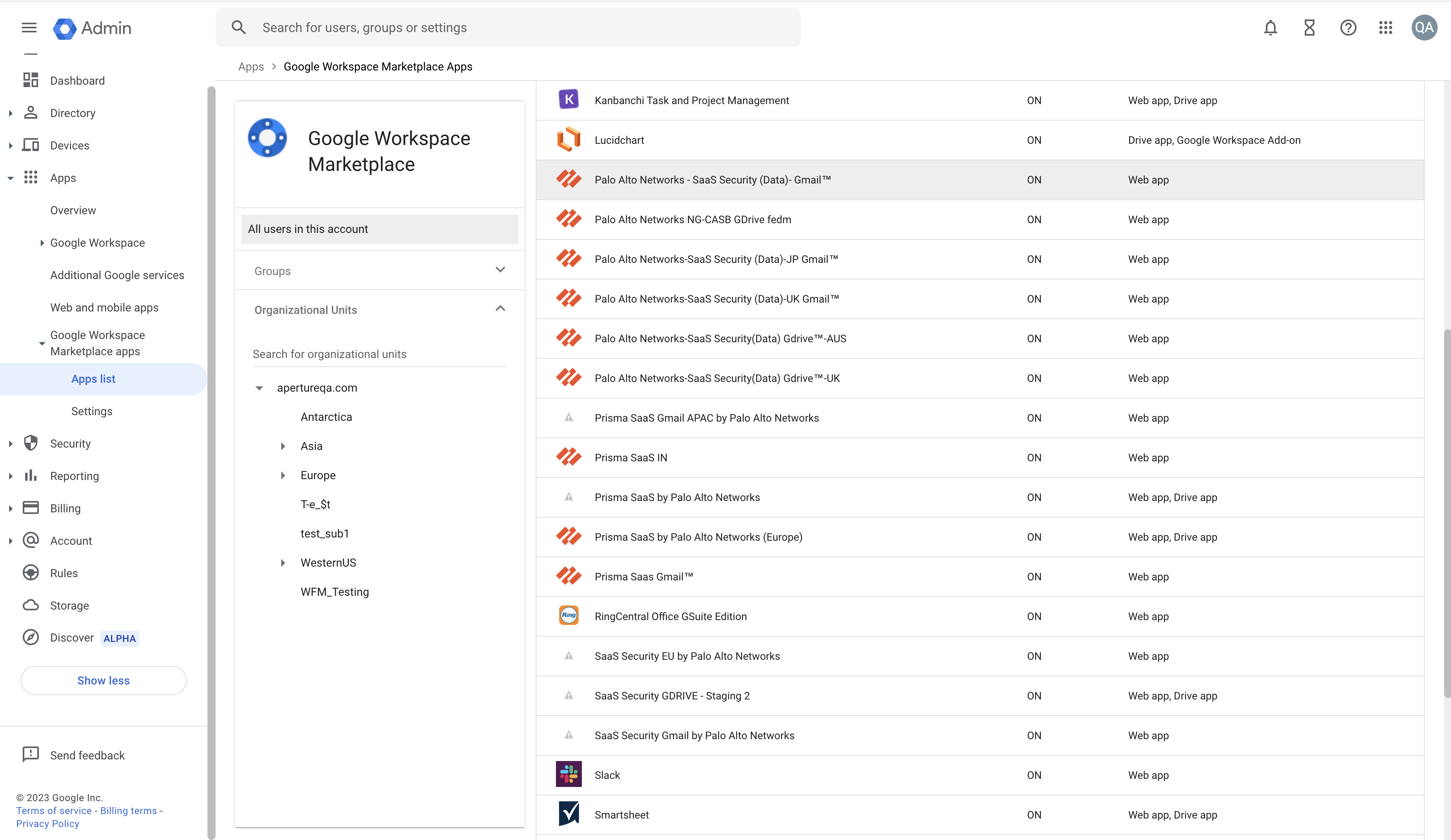
- Check if the Palo Alto Networks application is listed in the list of Google
Workspace Marketplace Apps. Following are the app names for specific regions:
- India region: NG CASB Gdrive IN
- Australia region: Palo Alto Networks Gdrive- Aus
- Japan region: Palo Alto Networks Gdrive- JP
- UK region: Palo Alto Networks Gdrive- UK
- Europe region: Prisma SaaS by Palo Alto Networks
- Asia-Pacific region: Prisma SaaS by Palo Alto Networks (Asia-Pacific )
- VPC region: Prisma SaaS by Palo Alto Networks
- FEDM region: Palo Alto Networks -SaaS Security Gdrive-FEDM
![]()
Handling ErrorsTo understand your error messages and ways to resolve them, see:- Common Errors
- User Permission Errors: Ensure that the user is a Super Admin in the Google console.
- App Authentication Failure (unauthorized_client error): Domain Wide delegation isn’t provided or the application is not installed in the Google Dashboard.
- Errors in App Authentication
- Errors during fetching sample data assets and sample user activities
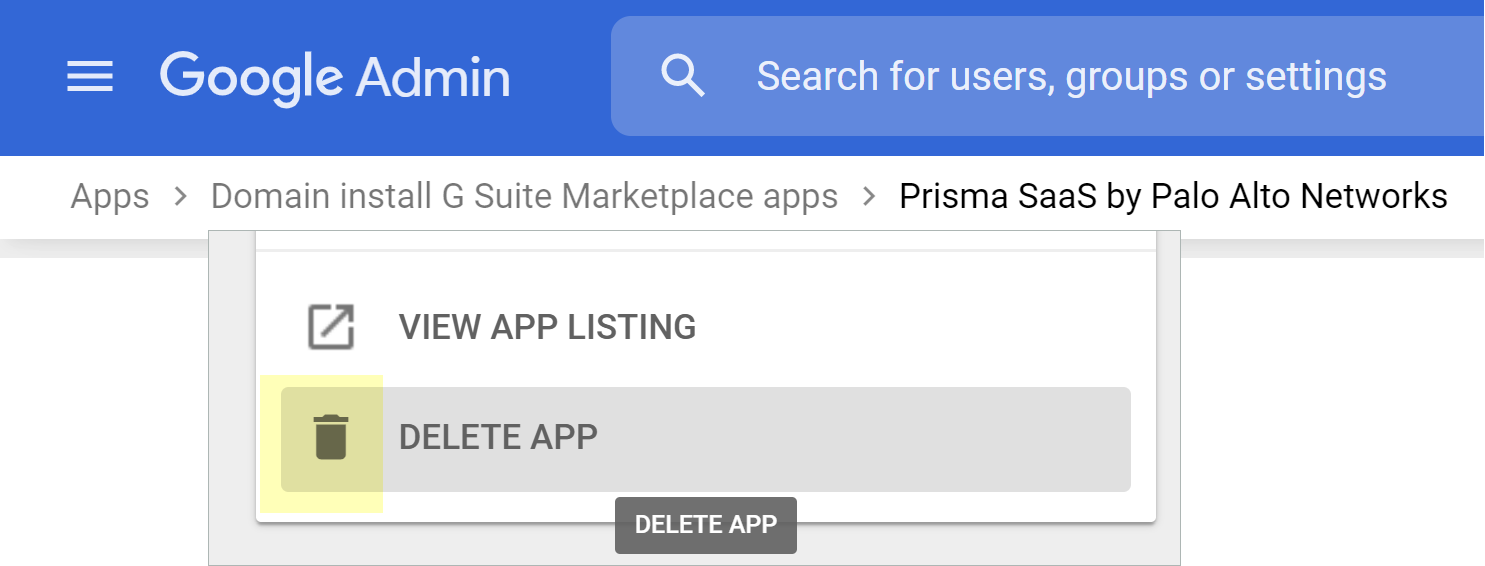
The other most common issues related to onboarding a Google Drive app are as follows:SymptomExplanationSolutionWhen you click Connect to Google Drive Account (Step 3 of Install page), you receive an authentication error.The Google account doesn’t have sufficient permissions to authenticate and access all the assets within Google Drive.Make sure your Google account is an administrator with default super admin role or applicable custom role with the permission outlined in Prerequisites to be completed on Google Drive.When you click Connect to Google Drive Account (Step 3 of Install page), you receive a login error: This email must be added as a Super AdminThe Google account doesn’t have an administrator account in Data Security.Make sure your Google account is super admin on Data Security as outlined in Prerequisites to be completed on Google Drive..When you click Connect to Google Drive Account (Step 3 of the Install page), you’re redirected to a product landing page, and the Google Drive app doesn’t appear in the Cloud Apps list.![]() Cached files are preventing the correct redirect.Don't log out of Data Security. Instead, open Data Security in an incognito window. Repeat the onboarding process and click on Connect to Google Drive Account again. The Google Drive app now appears in the Cloud app list.When click on Go to Google Marketplace (Step 2 in the Install page), an Please uninstall app for domain in Admin Console message displays.
Cached files are preventing the correct redirect.Don't log out of Data Security. Instead, open Data Security in an incognito window. Repeat the onboarding process and click on Connect to Google Drive Account again. The Google Drive app now appears in the Cloud app list.When click on Go to Google Marketplace (Step 2 in the Install page), an Please uninstall app for domain in Admin Console message displays.![]() This problem usually occurs if you previously installed the app and deleted it from Data Security but did not delete it from Google Marketplace.Delete the app from the Google Marketplace, then you’ll be able to add the Google Drive app in Data Security.
This problem usually occurs if you previously installed the app and deleted it from Data Security but did not delete it from Google Marketplace.Delete the app from the Google Marketplace, then you’ll be able to add the Google Drive app in Data Security.![]() This problem occurs if you complete step 2 of Install page and either abort your install or forget to click Connect to Google Drive Account (Step 3 of Install page).If the Google Marketplace page is open in the same browser and session that you used when you initially added the Google Drive app, simply click Connect to Google Drive Account.Otherwise, delete the Google Drive app from the Google Marketplace and repeat the Google Drive app onboarding process in Data Security.
This problem occurs if you complete step 2 of Install page and either abort your install or forget to click Connect to Google Drive Account (Step 3 of Install page).If the Google Marketplace page is open in the same browser and session that you used when you initially added the Google Drive app, simply click Connect to Google Drive Account.Otherwise, delete the Google Drive app from the Google Marketplace and repeat the Google Drive app onboarding process in Data Security.![]() If the issue persists, contact SaaS Security Technical Support.
If the issue persists, contact SaaS Security Technical Support.Fix Google Drive User Activities Monitoring Issues
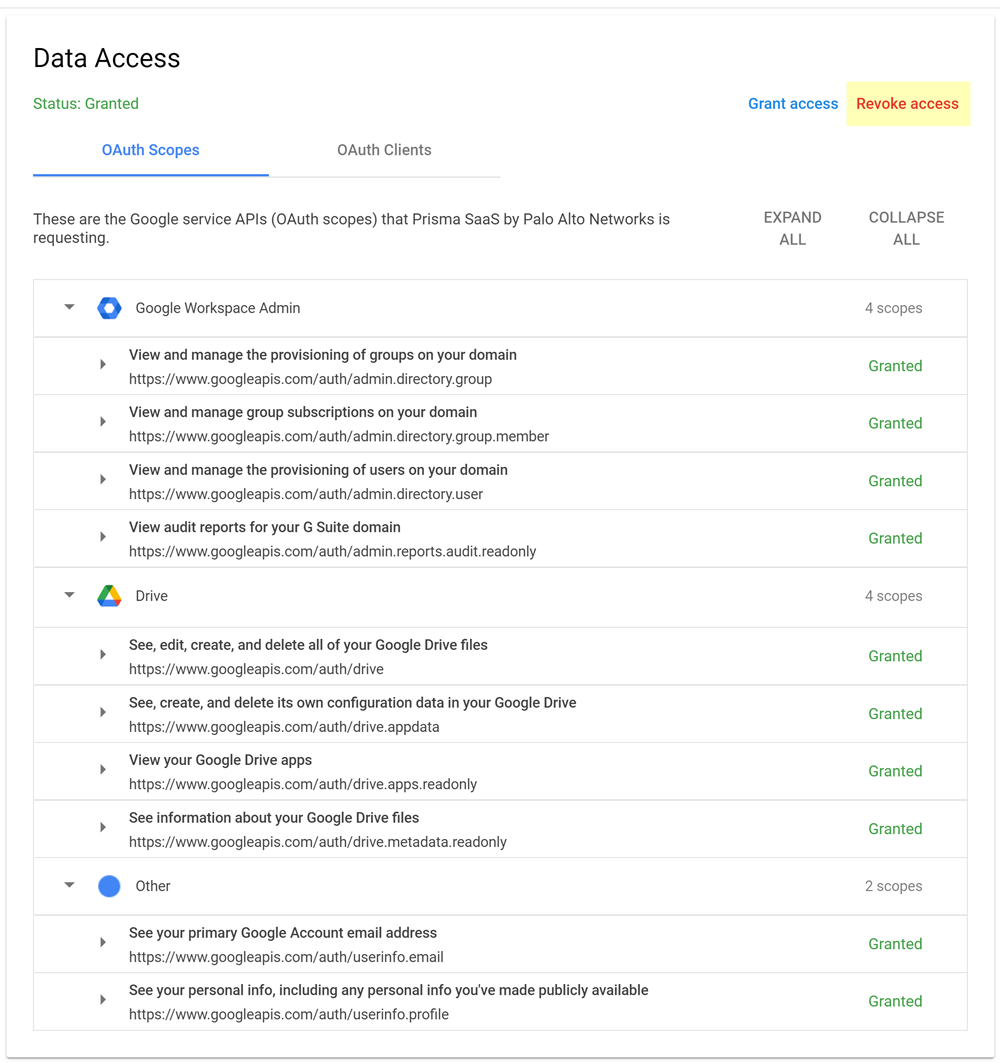
If user activities for Google Drive don't display in Data Security, contact SaaS Security Technical Support to initiate appropriate troubleshooting steps. However, if requested to do so by Data Security Technical Support due to permissions issues, remove the API client access from Google, then authenticate the Google app to enable the access again.- Open a web browser and log in to admin.google.com.Select Google Workspace Marketplace appsApps list.Click on Prisma SaaS by Palo Alto Networks in the list.Select Data AccessOAuth ScopesSelect Revoke access.
![]()
Selective Scanning on Google Drive App
Customizations include modifying a Google Drive app name and specifying OUs.- (Optional) Give a descriptive name to this app instance.
- Select the Google Drive link on the Cloud Apps list.Enter a descriptive Name to differentiate this instance of Google Drive from other instances you're managing.(Optional) Enter the Organizational Units for OU scanning.OU scanning on Google Drive is distinct from group‑based selective scanning, which is for supported cloud apps that use Azure Active Directory Services. However, the use cases are the same. Ensure that you have completed the following three steps before performing selective scanning:You can enter multiple OUs including the OU name and sub-OU:
- /—Top level of a newly added Google App
- blank—Top level of an existing Google App
- /Asia—A child OU of the top-level OU
- /Asia/China—China is a child OU of the Asia OU
- /Asia/India, /Europe—India is a child OU of the Asia OU and Europe is a child OU of the top-level OU
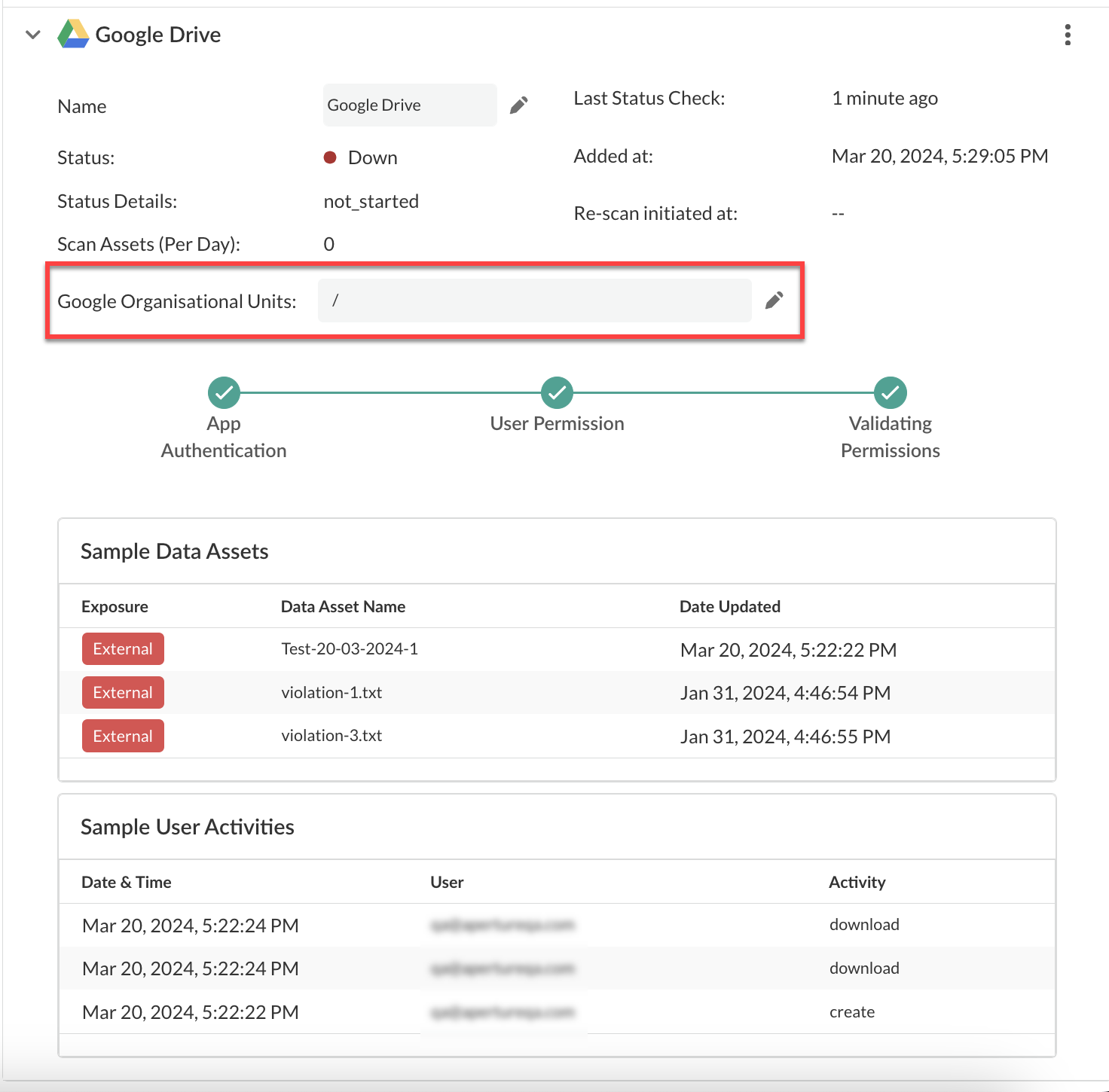
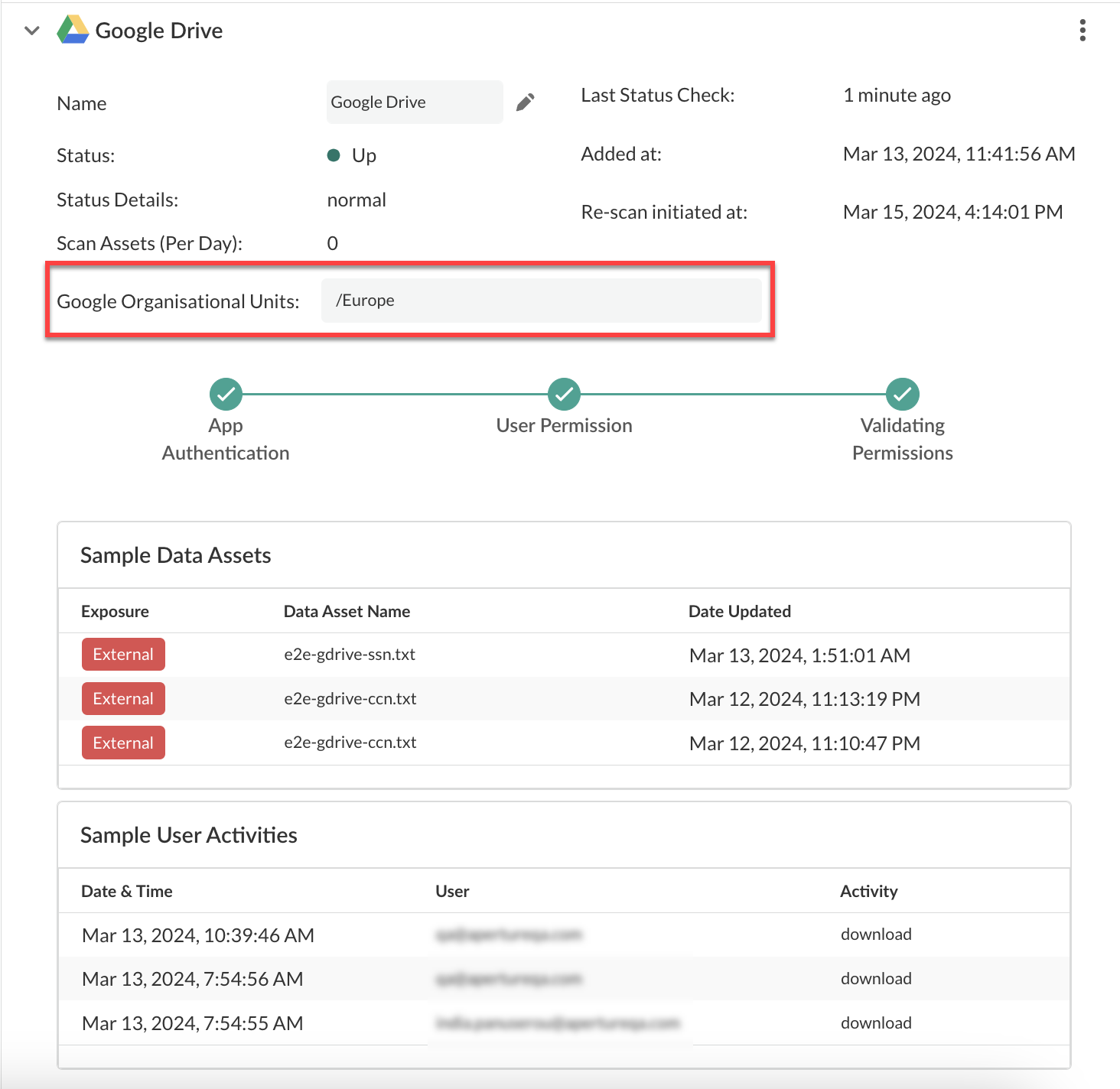
For example, your domain is companydomain.com and you want to scan three OUs—finance, operations, and marking and social media OUs. Enter the OUs as a comma-separated list: /finance,/operations,/marketing/socialmedia. If you leave this field blank, all units are scanned.Backward scans and forward scans detect OU assets by querying the OUs for users, then querying for each user’s file ownership. A file is ignored if it exists in a folder that is owned by an OU user even if the file is owned by a non-OU user. However, if file ownership is subsequently changed to the OU user then the incremental scan discovers the file. The forward scan detects any changes to the OU configuration, including OUs that you add or delete in the OU scanning configuration or users who you add, move, or delete from OUs on Google Drive.![]() If you're using Strata Cloud Manager, the Google Organizational Units can’t be edited once the app has started scanning as seen in the following screenshot .
If you're using Strata Cloud Manager, the Google Organizational Units can’t be edited once the app has started scanning as seen in the following screenshot .![]() Next step: Proceed to Start Scanning and Monitor Results.
Next step: Proceed to Start Scanning and Monitor Results.Start Scanning and Monitor Results
When you add a new cloud app and enable scanning, Data Security automatically scans the cloud app against the default data patterns and displays the match occurrences. You can take action now to improve your scan results and identify risks.- To start scanning the new Google Drive app for risks, select ConfigurationSaaS SecurityData SecurityApplicationsGoogle DriveView Settings...Start Scanning.Monitor the scan results.During the discovery phase, Data Security scans files and matches them against enabled default policy rules.Verify that your default policy rules are effective. If the results don’t capture all the risks or you see false positives, proceed to the next step.(Optional) Modify match criteria for existing policy rules.(Optional) Add new policy rules.Consider the business use of your app, then identify risks unique to your enterprise. As necessary, add new:(Optional) Configure or edit a data pattern.You can Configure Data Patterns to identify specific strings of text, characters, words, or patterns to make it possible to find all instances of text that match a data pattern you specify.
Google Drive App Behaviors
The most common behaviors related to the Google Drive app are as follows:SymptomExplanationSolutionWhen you view a Goggle Drive asset in Data Security, the Created date indicates a more current date than the Last Updated date.lastModified (Last Updated) is the date that the file is modified locally by the user and the createDate (Created) is the date that the file is uploaded (aka cloud-created) in Google Drive.This behavior is expected due to how the Google Drive API determines timestamps.When a user moves a file from Shared Drives to My Drive or vice versa, Data Security displays Delete in the Activity log.Google API reported the action as a Delete when actually Google did in fact Move the file. Data Security displays in the Activity Log what the Google API reports.No known solution at this time. We communicate with our Google partner on an ongoing basis regarding its API.Some files are shared with internal users, but Data Security indicates External.For Google shared drives, Data Security analyzes a file’s direct collaborators and the drive’s members. If one of the members is external, Data Security assigns an External exposure level.This behavior is expected and by design.Create Domain Wide Delegation
You need domain wide delegation to make API calls to Google and fetch user data. To implement domain wide delegation, perform the following steps.Domain wide delegation is applicable only for Australia, UK, Japan, India, and FEDM regions.- Log in to the Google Admin Console as a superuser and select SecurityAccess and data controlAPI controlsMANAGE DOMAIN WIDE DELEGATIONAdd new.Enter your client ID that’s applicable for your region.
- AU: 117916877802214783504
- UK: 110579143651113261020
- IN: 101485368660522582034
- JP: 105441676635767149048
- FEDM: 107464171233791181403
Enter the following comma-delimited OAuth scopes and click AUTHORIZE.- https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.email
- https://www.googleapis.com/auth/userinfo.profile
- https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.group
- https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.group.member
- https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user
- https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user.readonly
- https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user.security
- https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.reports.audit.readonly
- https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive
- https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.appdata
- https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.apps.readonly
- https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.metadata.readonly