Administrative Roles
Table of Contents
Expand all | Collapse all
-
- Set Up the Endpoint Infrastructure
- Activate Traps Licenses
-
- Endpoint Infrastructure Installation Considerations
- TLS/SSL Encryption for Traps Components
- Configure the MS-SQL Server Database
- Install the Endpoint Security Manager Server Software
- Install the Endpoint Security Manager Console Software
- Manage Proxy Communication with the Endpoint Security Manager
- Load Balance Traffic to ESM Servers
-
- Malware Protection Policy Best Practices
- Malware Protection Flow
- Manage Trusted Signers
-
- Remove an Endpoint from the Health Page
- Install an End-of-Life Traps Agent Version
-
-
- Traps Troubleshooting Resources
- Traps and Endpoint Security Manager Processes
- ESM Tech Support File
-
- Access Cytool
- View the Status of the Agent Using Cytool
- View Processes Currently Protected by Traps Using Cytool
- Manage Logging of Traps Components Using Cytool
- Restore a Quarantined File Using Cytool
- View Statistics for a Protected Process Using Cytool
- View Details About the Traps Local Analysis Module Using Cy...
- View Hash Details About a File Using Cytool
Administrative Roles
Role-based access control (RBAC) enables you to use
preconfigured or define custom roles to assign access rights to
administrative users. Each role extends specific privileges to users
you assign to the role and each privilege defines access to specific
configuration settings and pages within the ESM Console. By customizing
a role and assigning specific privileges, you can enforce the separation
of information among functional or regional areas of your organization
to protect the privacy of data on the ESM Console.
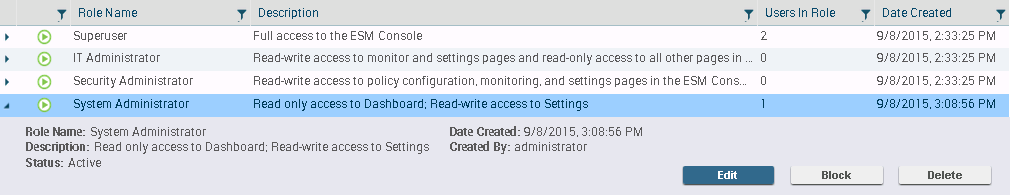
The way you configure administrative access depends on the security
requirements of your organization. Use roles to assign specific
access privileges to administrative user accounts. By default, the
ESM Console has built-in roles with specific access rights that
cannot be changed. When new features are added to the product, the
ESM Console automatically adds new features to the default role
definitions. The following table lists built-in roles and the access
privileges associated with each:
Role | Privileges |
|---|---|
Superuser | Full read-write access to the ESM Console. |
IT Administrator | Read-write access to monitor and configuration
settings pages and read-only access to all other pages in the ESM
Console; does not include the ability to disable all protection. |
Security Administrator | Read-write access to policy configuration,
monitoring, and settings pages in the ESM Console, including the
ability to disable all protection. This role also includes read-only access
to the agent health pages but no access to the server health or
licenses pages. |
While you cannot change the privileges associated with the built-in
roles, you can create custom roles that provide more granular access
control over the functional areas of the web interface. For these
roles, you can assign read-write access, read-only access, or no
access to all the ESM Console configuration functions and pages.
An example use of a custom role is security administrators who
need to be able to view logs about the status of endpoints but who
do not need to configure security rules.
