Manage Trusted Signers
Table of Contents
Expand all | Collapse all
-
- Set Up the Endpoint Infrastructure
- Activate Traps Licenses
-
- Endpoint Infrastructure Installation Considerations
- TLS/SSL Encryption for Traps Components
- Configure the MS-SQL Server Database
- Install the Endpoint Security Manager Server Software
- Install the Endpoint Security Manager Console Software
- Manage Proxy Communication with the Endpoint Security Manager
- Load Balance Traffic to ESM Servers
-
- Malware Protection Policy Best Practices
- Malware Protection Flow
- Manage Trusted Signers
-
- Remove an Endpoint from the Health Page
- Install an End-of-Life Traps Agent Version
-
-
- Traps Troubleshooting Resources
- Traps and Endpoint Security Manager Processes
- ESM Tech Support File
-
- Access Cytool
- View the Status of the Agent Using Cytool
- View Processes Currently Protected by Traps Using Cytool
- Manage Logging of Traps Components Using Cytool
- Restore a Quarantined File Using Cytool
- View Statistics for a Protected Process Using Cytool
- View Details About the Traps Local Analysis Module Using Cy...
- View Hash Details About a File Using Cytool
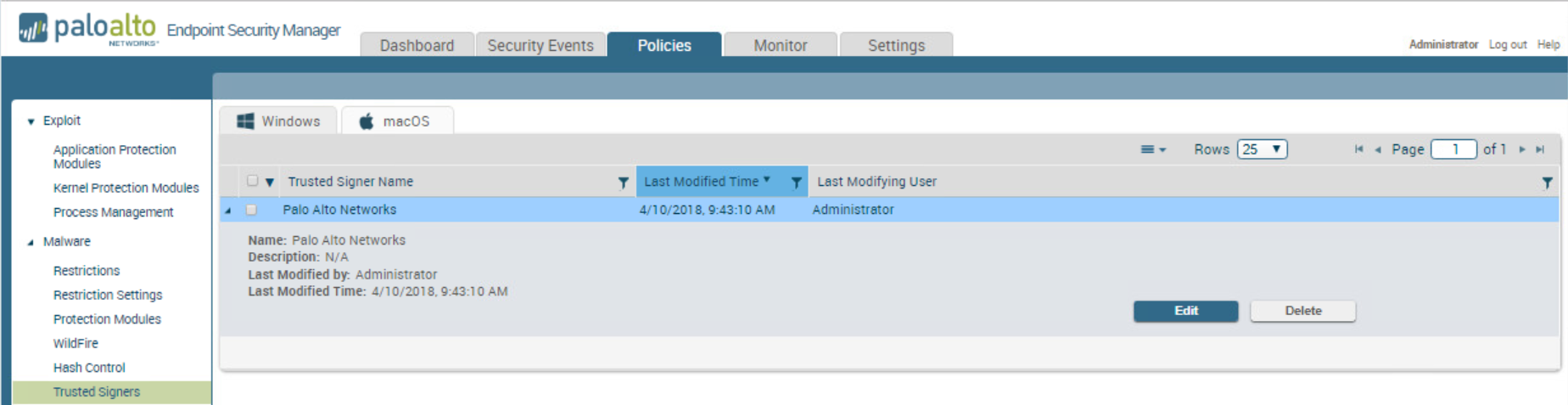
Manage Trusted Signers
Palo Alto Networks regularly reviews and makes
changes to the list of trusted signers and makes the list available
with the default security policy. Any updates to the list of trusted
signers are made available with content updates that you can obtain
from the Support portal (for more information,
see Content
Updates). You can also define your own trusted signers from
the ESM Console. For Windows signers, adding a trusted signer adds
the signer to the list of highly trusted signers. Traps evaluates
trusted signers according to the Malware Protection Flow.
To view and configure
trusted signers, your role must have the Trusted Signers privilege
enabled.
To whitelist a trusted signer:
- Select PoliciesMalwareTrusted Signers.
- Select the platform, Windows or Mac.
- Select the action menu, and Add Signer.
- Enter the name of the trusted signer.
- (Mac only) Specify the SHA1 hash of the certificate
that signs the file.To identify the hash for a certificate that signs a file, review the local agent logs after a file runs on the endpoint:
- Using Cytool, set the log level for the trapsd daemon
log to 7 (debug).
Traps-Mac:bin Traps$ sudo /Library/Application\ Support/PaloAltoNetworks/Traps/bin/cytool log 7 trapsd - Open the trapsd log and search for the name of the
file for which you want to identify the certificate hash.The “CertificateHash” field identifies the hash value. For example:
Traps-Mac:bin Traps$ open /var/log/traps/trapsd.log [...] “PublisherMatch” : { “CertificateHash” : “e86867eab7456a4fefcda5541be7d7e2c5aacbe9”, “PublisherName” : “software (483dwkw443)” }, “SecurityEventReported” : false, “hash” : “7a11be65b9a8c60fa22dac612125e897a89f6f72228abe74514920618642c4e5" }
- Using Cytool, set the log level for the trapsd daemon
log to 7 (debug).
- (Optional) Provide a description indicating why you whitelisted the signer.
- Save the trusted signer.After you save a trusted signer, you can edit or delete it at any time.The ESM Console logs any changes to the trusted signers list and displays those logs from the MonitorESMHealth page. To filter for changes to the trusted signers, filter the Report Type column for any of the reports which begin with Trusted Signer.
