Manage Global Whitelists
Table of Contents
Expand all | Collapse all
-
- Set Up the Endpoint Infrastructure
- Activate Traps Licenses
-
- Endpoint Infrastructure Installation Considerations
- TLS/SSL Encryption for Traps Components
- Configure the MS-SQL Server Database
- Install the Endpoint Security Manager Server Software
- Install the Endpoint Security Manager Console Software
- Manage Proxy Communication with the Endpoint Security Manager
- Load Balance Traffic to ESM Servers
-
- Malware Protection Policy Best Practices
- Malware Protection Flow
- Manage Trusted Signers
-
- Remove an Endpoint from the Health Page
- Install an End-of-Life Traps Agent Version
-
-
- Traps Troubleshooting Resources
- Traps and Endpoint Security Manager Processes
- ESM Tech Support File
-
- Access Cytool
- View the Status of the Agent Using Cytool
- View Processes Currently Protected by Traps Using Cytool
- Manage Logging of Traps Components Using Cytool
- Restore a Quarantined File Using Cytool
- View Statistics for a Protected Process Using Cytool
- View Details About the Traps Local Analysis Module Using Cy...
- View Hash Details About a File Using Cytool
Manage Global Whitelists
To allow executable files to run from local
folders and external media and allow child processes initiated from parent
processes in a specific folder, you can configure a global whitelist.
Similar to the existing whitelist functionality for Java processes,
unsigned executable files, and Thread Injection, you can specify
full paths and path variables and can also use wildcards for pattern
matching (% to match similar terms and * to
match any characters).
Items in the whitelist section also
take precedence over any blacklisted items and are evaluated first
in the security policy.
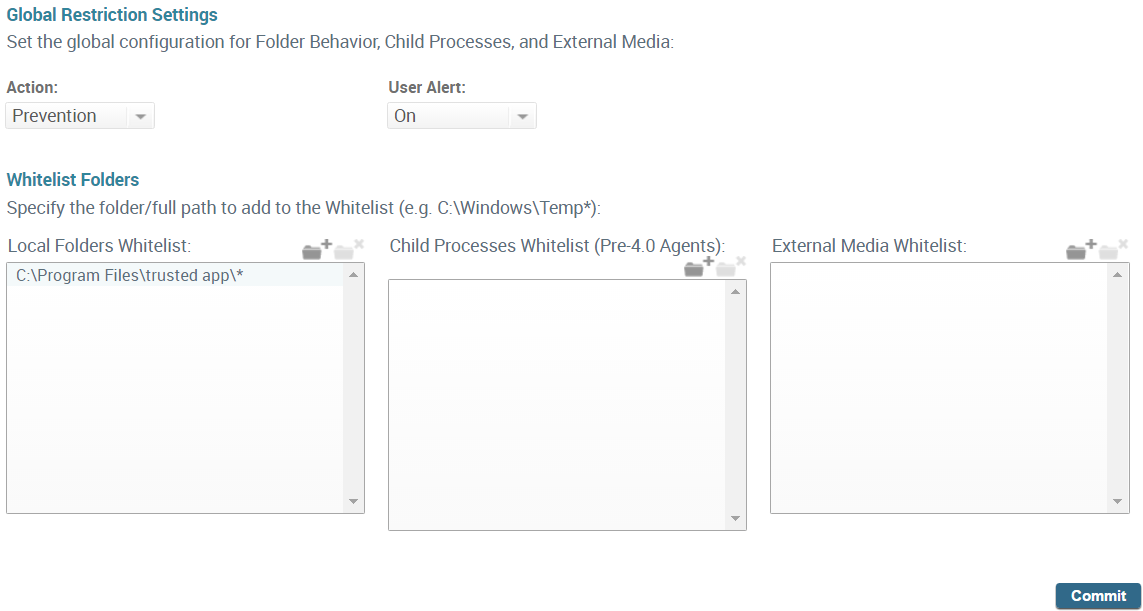
- Select PoliciesMalwareRestriction Settings.
- To specify whether Traps blocks an executable file that
it is opened from a location not included in the whitelist or that
is younger than the block period, configure the Action as
one of the following:
- Notification—Do not block access to executable files and processes but log when files that are opened from locations not included in the whitelist and report those events to the ESM.or
- Prevention—Block executable files and processes.
- To specify whether Traps should notify the user when
an executable file is opened from a location not included in the
whitelist, configure the User Alert as one
of the following:
- On—Notify the user.or
- Off—Do not notify the user.
- Click the add folder icon next to the whitelist area for Local Folder, Child Process, or Media Control and enter the full path or partial path. For example, C:\Windows\filename.exe.
![]() Whitelists also support wildcards and environmental variables, such as %windir% (for more details, see Wildcards and Variables in Policy Rules).
Whitelists also support wildcards and environmental variables, such as %windir% (for more details, see Wildcards and Variables in Policy Rules). - Click Commit to save your changes.
