Decryption Log Errors, Error Indexes, and Bitmasks
Table of Contents
End-of-Life (EoL)
Decryption Log Errors, Error Indexes, and Bitmasks
View and interpret certificate, cipher, protocol, version,
and other TLS handshake errors to troubleshoot decryption issues.
The Error Index and Error columns
in the Decryption log provide information about the decryption error
category and details, respectively. You can also see error and error
index information in the Handshake Details section of the Detailed
Log View (click
![]() for any log entry).
The Decryption log Error Index indicates
one of eight error categories:
for any log entry).
The Decryption log Error Index indicates
one of eight error categories:
| Error Index | Error (possible errors shown for the Error Index) |
|---|---|
| Certificate | Errors such as invalid certificates, expired certificates,
unsupported client certificates, OCSP/CRL check revocations and
failures, untrusted issuer CAs (sessions signed by an untrusted
root, which includes incomplete certificate chains), and other certificate
errors. When the firewall doesn’t have an intermediate
certificate because the site did not send the full certificate chain,
you can find and install the missing certificate to Repair Incomplete Certificate Chains. |
| Cipher | Unsupported cipher errors where:
The error
message includes the supported client cipher bitmask value and the
supported Decryption profile cipher bitmask value. Use the bitmask
values to identify the cipher the client tried to use and to list
the cipher values that the Decryption profile supports as described
later in this topic. |
| Feature | Errors such as oversized TLS handshakes or unknown handshakes, oversized
certificate chains (more than five certificates), and other unsupported features. |
| HSM | Hardware storage module (HSM) errors such as unknown
requests, items not found in the configuration, request timeouts,
and other HSM errors and failures. |
| Protocol | Errors such as TLS handshake failures, private and public
key mismatches, Heartbleed errors, TLS key exchange failures, and
other TLS protocol errors. Protocol errors show when the server
doesn’t support the protocols that the client supports, the server
uses certificate types that the firewall doesn’t support, and general
TLS protocol errors. |
| Resource | Errors such as lack of sufficient memory. |
| Resume | Session resumption errors concerning resume session
IDs and tickets, resume session entries in the firewall cache, and
other session resumption errors. |
| Version | Errors regarding client and Decryption profile version
mismatches and client and server version mismatches. The
error message includes bitmask values that identify the supported client
and Decryption profile versions. Use the bitmask values to identify
the cipher the client tried to use and to list the cipher values
that the Decryption profile supports as described later in this
topic. |
If no suitable error description category exists for an
error, the default message is General TLS protocol error.
Version and cipher log error information includes bitmask values
that you convert to actual values using operational CLI commands:
- Version error bitmask values identify mismatches between the TLS protocol versions that the client and server use and also identify TLS protocol mismatches between the client and the Decryption profile applied to the traffic. The CLI command to convert version error bitmasks is:
admin@vm1>debug dataplane show ssl-decrypt bitmask-version <bitmask-value>The command returns the TLS version that matches the bitmask. - Cipher error bitmask values identify encryption and other mismatches between the client and the Decryption profile applied to the traffic.
admin@vm1>debug dataplane show ssl-decrypt bitmask-cipher <bitmask-value>The command returns the cipher that matches the bitmask.
Filter the Decryption log to find version and cipher errors,
plug the bitmask values for sessions with errors into the appropriate
CLI command, obtain the values of the protocol version or cipher
that caused the error, and use the information to update the Decryption
policy or profile if you want to allow access to the site in question.
Version Errors
To identify and fix version mismatch errors:
- Filter the Decryption Log to identify version errors using the filter (err_index eq Version). The highlighted values are bitmask values:
![]() You can filter the Decryption log in many ways. For example, to see only TLSv1.3 version errors, use the filter (err_index eq Version) and (tls_version eq TLS1.3):
You can filter the Decryption log in many ways. For example, to see only TLSv1.3 version errors, use the filter (err_index eq Version) and (tls_version eq TLS1.3):![]()
- Log in to the CLI and look up the bitmask values. The version errors in the first screen shot (the same errors for all three sessions) show an issue with a client and Decryption profile mismatch—the supported client version bitmask is 0x08 and the supported Decryption profile version bitmask is 0x70:
admin@vm1>debug dataplane show ssl-decrypt bitmask-version 0x08TLSv1.0
This output shows that the client supports only TLSv1.0.admin@vm1>debug dataplane show ssl-decrypt bitmask-version 0x70TLSv1.1TSLv1.2TLSv1.3This output shows that the Decryption profile supports TLSv1.1, TLSv1.2, and TLSv1.3, but not TLSv1.0. Now you know the issue is that the client only supports a very old version of the TLS protocol and the Decryption profile attached to the Decryption policy rule that controls the traffic does not allow TLSv1.0 traffic.The next thing to do is to decide what action to take. You could update the client so that it accepts a more secure TLS version. If the client requires TLSv1.0 for some reason, you can continue let the firewall continue to block the traffic, or you can update the Decryption profile to allow all TLSv1.0 traffic (not recommended), or you can create a Decryption policy and profile that allow TLSv1.0 and apply it only to the client devices that must use TLSv1.0 and cannot support a more secure protocol (most secure option for allowing the traffic).The version error in the second screen shot shows a different issue: a client and server version mismatch. The error indicates the supported client bitmask as 0x20:admin@vm1>debug dataplane show ssl-decrypt bitmask-version 0x20TLSv1.2The output shows that the client supports only TLSv1.2. Since the server does not support TLSv1.2, it may only support TLSv1.3 or it may support only TLSv1.1 or lower (less secure protocols). You can use Wireshark or another packet analysis tool to find out which version of TLS the server supports. Depending on what the server supports, you can:- If the server only supports TLSv1.3, you could edit the Decryption profile so that it supports TLSv1.3.
- If the server only supports TLSv1.1 or lower, evaluate whether you need to access that server for business reasons. If not, consider blocking the traffic to increase security. If you need to access the server for business purposes, create or add the server to a Decryption policy that applies only to the servers and sites you need to access for business; don’t allow access to all servers that use less secure TLS versions.
- To find the Decryption policy that controls the session traffic, check the Policy Name column in the log (or click the magnifying glass iconnext to the Decryption log to see the information in the General section of the Detailed Log View). In the example above, the Decryption policy name is Big Brother. To find the Decryption policy and profile, go to PoliciesDecryption, select the policy named Big Brother, and then select the Options tab. Decryption profile displays the name of the Decryption profile.
![]() Go to ObjectsDecryptionDecryption Profile, select the appropriate Decryption profile, and edit it to address the version issue.
Go to ObjectsDecryptionDecryption Profile, select the appropriate Decryption profile, and edit it to address the version issue.
Cipher Errors
Using the Decryption log to hunt down cipher errors
is similar to hunting down version errors—you filter the log to
find errors and obtain error bitmasks. Then you go to the CLI, convert
the bitmask to the error value, and then take appropriate action
to fix the issue. For example:
- Filter the Decryption Log to identify cipher errors using the filter (err_index eq Cipher). For example, let’s examine a cipher error with the Error message Unsupported cipher. Supported client cipher bitmask: 0x80000000. Support decrypt profile cipher bitmask 0x60f79980.
- Log in to the CLI and look up the bitmask values:
admin@vm1>debug dataplane show ssl-decrypt bitmask-cipher 0x80000000CHACHA_PLY1305_SHA256This output shows that client tried to negotiate a cipher that the firewall supports (if the bitmask is all zeros (0x0000000, then the client tried to negotiate a cipher that the firewall doesn’t support):admin@vm1>debug dataplane show ssl-decrypt bitmask-cipher 0x80000000TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA TLS13_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 TLS13_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
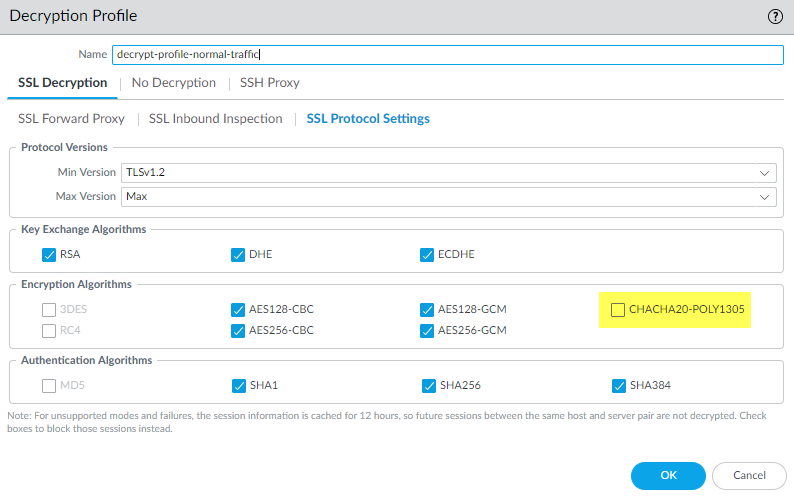
This output shows that the Decryption profile that controls the traffic supports many ciphers, but does not support the cipher the client is trying to use.To fix this issue so that the firewall allows and decrypts the traffic, you need to add support for the missing cipher to the Decryption profile. - Check the Decryption log or the Detailed Log View Policy Name to get the name of the Decryption policy that controls the traffic. Go to PoliciesDecryption and select the policy. On the Options tab, look up the name of the Decryption profile. Next, Go to ObjectsDecryptionDecryption Profile, select the appropriate Decryption profile, and edit it to address the version issue.In this example, the Decryption profile does not support the TLS13_WITH_CHACHA_POLY1305_SHA256 cipher, so the client can’t connect:
![]() To fix the issue, select the CHACHA20-POLY1305 encryption algorithm option (the Max Version setting of Max means that the profile already supports TLSv1.3 and the Authentication Algorithm setting already includes SHA256, so only the encryption algorithm support was missing) and then Commit the configuration. After you commit the configuration, the Decryption profile supports the missing cipher and the decryption sessions for the traffic succeed.If the firewall does not support a cipher suite and you need to allow the traffic for business purposes, create a Decryption policy and profile that applies only to that traffic. In the Decryption profile, disable the Block sessions with unsupported cipher suites option.
To fix the issue, select the CHACHA20-POLY1305 encryption algorithm option (the Max Version setting of Max means that the profile already supports TLSv1.3 and the Authentication Algorithm setting already includes SHA256, so only the encryption algorithm support was missing) and then Commit the configuration. After you commit the configuration, the Decryption profile supports the missing cipher and the decryption sessions for the traffic succeed.If the firewall does not support a cipher suite and you need to allow the traffic for business purposes, create a Decryption policy and profile that applies only to that traffic. In the Decryption profile, disable the Block sessions with unsupported cipher suites option.
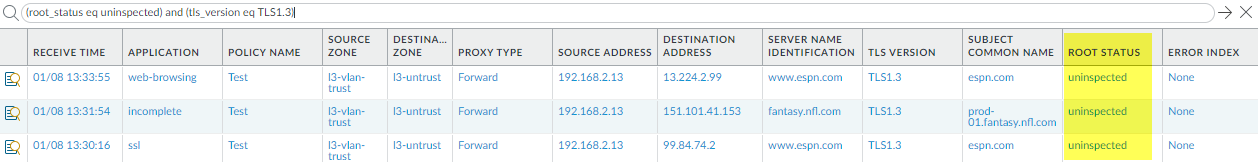
Root Status “Uninspected”
In some cases, the Root
Status column displays the value uninspected.
There are a number of reasons why the firewall could not inspect
the root status, including:
- Session resumption.
- Traffic was not decrypted because a No Decryption policy controlled the traffic, so the firewall did not decrypt the traffic.
- A decryption failure occurred before the firewall could inspect the server certificate.
Filter the Decryption Log (root_status eq uninspected) and (tls_version eq TLS1.3) to
see Decryption sessions for which the Root Status is uninspected: