Repair Incomplete Certificate Chains
Table of Contents
End-of-Life (EoL)
Repair Incomplete Certificate Chains
Locate and install missing intermediate certificates
to fix incomplete certificate chains using the Decryption log.
Not all websites send their complete certificate
chain even though the RFC 5246 TLSv1.2 standard requires
authenticated servers to provide a valid certificate chain leading
to an acceptable certificate authority. When you enable decryption
and apply a Forward Proxy Decryption profile that enables Block
sessions with untrusted issuers in the Decryption policy,
if an intermediate certificate is missing from the certificate list the
website’s server presents to the firewall, the firewall can’t construct
the certificate chain to the top (root) certificate. In these cases,
the firewall presents its Forward Untrust Certificate to the client
because the firewall cannot construct the chain to the root certificate
and trust cannot be established without the missing intermediate
certificate.
The firewall only has root certificates
in its Default Trusted Certificate Authorities store.
If
a website you need to communicate with for business purposes has
one or more missing intermediate certificates and the Decryption
profile blocks sessions with untrusted issuers, then you can find
and download the missing intermediate certificate and install it
on the firewall as a Trusted Root CA so that the firewall trusts the
site’s server. (The alternative is to contact the website owner
and ask them to configure their server so that it sends the intermediate
certificate during the handshake.)
If you allow sessions
with untrusted issuers in the Decryption profile, the firewall establishes
sessions even if the issuer is untrusted; however, it is a best
practice to block sessions with untrusted issuers for better security.
- Find websites that cause incomplete certificate chain errors.
- Filter the Decryption log to identify Decryption sessions that failed because of an incomplete certificate chain.In the filter field, type the query (err_index eq Certificate) and (error contains ‘http’). This query filters the logs for Certificate errors that contain the string “http”, which finds all of the error entries that contain the CA Issuer URL (often called the URI). The CA Issuer URL is the Authority Information Access (AIA) information for the CA Issuer.Click an Error column entry that begins “Received fatal alert UnknownCA from client. CA Issuer URL:” followed by the URI.
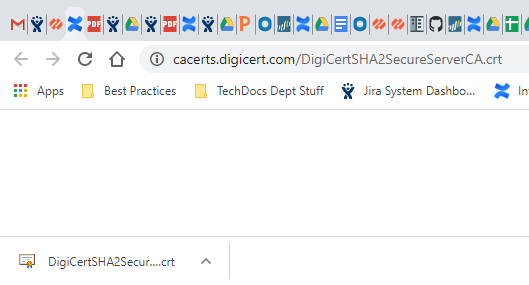
![]() The firewall automatically adds the selected error to the query and shows the full URI path (the full URI path may be truncated in the Error column).Copy and paste the URI into your browser and then press Enter to download the missing intermediate certificate.
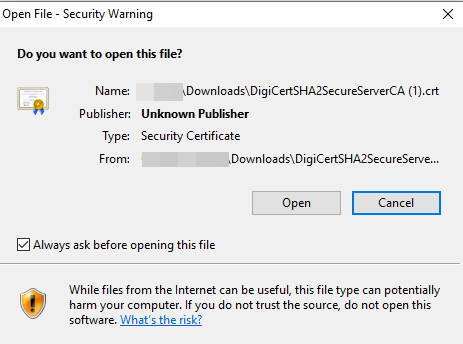
The firewall automatically adds the selected error to the query and shows the full URI path (the full URI path may be truncated in the Error column).Copy and paste the URI into your browser and then press Enter to download the missing intermediate certificate.![]() Click the certificate to open the dialog box.
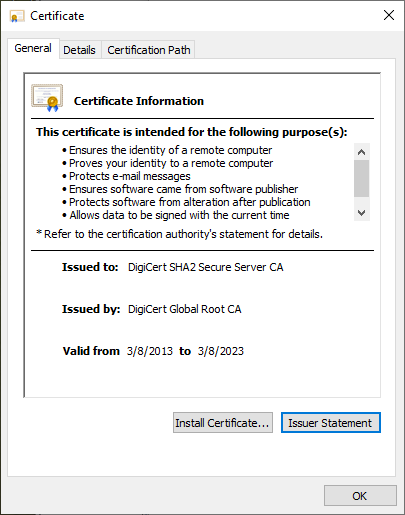
Click the certificate to open the dialog box.![]() Click Open to open the certificate file.
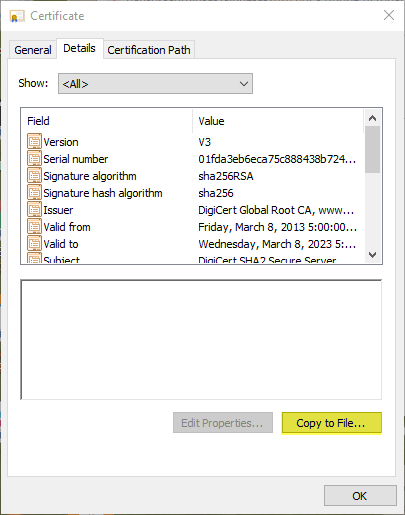
Click Open to open the certificate file.![]() Select the Details tab and then click Copy to File....
Select the Details tab and then click Copy to File....![]() Follow the export directions. The certificate is copied to the folder you designated as you default download folder.Import the certificate into the firewall.
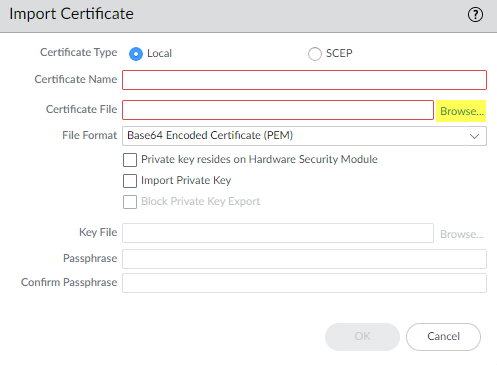
Follow the export directions. The certificate is copied to the folder you designated as you default download folder.Import the certificate into the firewall.- Navigate to DeviceCertificate ManagementCertificates and then select Import.Browse to the folder where you stored the missing intermediate certificate and select it. Leave the File Format as Base64 Encoded Certificate (PEM).
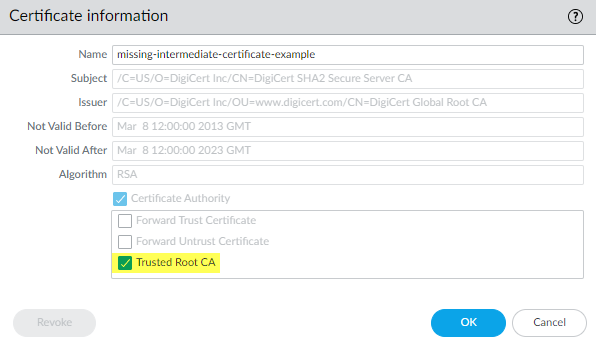
![]() Name the certificate and specify any other options you want to use, then click OK.When the certificate has imported, select the certificate from the Device Certificates list to open the Certificate Information dialog.Select Trusted Root CA to mark the certificate as a Trusted Root CA on the firewall and then click OK.
Name the certificate and specify any other options you want to use, then click OK.When the certificate has imported, select the certificate from the Device Certificates list to open the Certificate Information dialog.Select Trusted Root CA to mark the certificate as a Trusted Root CA on the firewall and then click OK.![]() In DeviceCertificate ManagementCertificatesDevice Certificates, the imported certificate now appears in the list of certificates. Check the Usage column to confirm that the status is Trusted Root CA Certificate to verify that the firewall considers the certificate to be a trusted root CA.Commit the configuration.You have now repaired the broken certificate chain.The firewall doesn’t block the traffic because the CA issuer is not untrusted anymore. Repeat this process for all missing intermediate certificates to repair their certificate chains.
In DeviceCertificate ManagementCertificatesDevice Certificates, the imported certificate now appears in the list of certificates. Check the Usage column to confirm that the status is Trusted Root CA Certificate to verify that the firewall considers the certificate to be a trusted root CA.Commit the configuration.You have now repaired the broken certificate chain.The firewall doesn’t block the traffic because the CA issuer is not untrusted anymore. Repeat this process for all missing intermediate certificates to repair their certificate chains.