Prisma Access
DNS for Prisma Access
Table of Contents
Expand All
|
Collapse All
Prisma Access Docs
-
- 6.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 6.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 5.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 4.2 Preferred
- 4.1 Preferred
- 4.0 Preferred
- 3.2 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.1 Preferred and Innovation
- 3.0 Preferred and Innovation
- 2.2 Preferred
-
-
- 4.0 & Later
- Prisma Access China
-
-
DNS for Prisma Access
Learn about DNS for Prisma Access.
| Where Can I Use This? | What Do I Need? |
|---|---|
|
|
Prisma Access allows you to specify DNS servers to resolve both domains that are internal to your
organization and external domains. Do this to provide access to services on your
corporate network—like LDAP and DNS servers—especially if you plan to set up service
connections to provide access to these type of resources at HQ or in data centers.
Prisma Access supports DNS resolution for mobile users- Global Protect and
remote networks deployments. DNS queries for domains in the Internal Domain
List are sent to your local DNS servers to ensure that resources are available to Prisma
Access remote network users and mobile users.
For example, if you want a DNS lookup for your corporate domain to go exclusively to the
corporate DNS server, specify the corporate domain and the corporate DNS servers here.
To ensure that endpoints use the DNS Proxy IP Address, they must
be configured to resolve DNS via the IP address shown in ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessPrisma Access InfrastructurePrisma Access DNS Proxy IP Address.
DNS for Prisma Access (Strata Cloud Manager)
Enable Prisma Access to resolve both internal and public
domains. You can choose to use Prisma Access DNS or let Prisma Access
leverage your organization’s DNS setup.
Here’s how to set up Prisma Access to resolve
internal domains, and how to customize DNS settings (to resolve
both internal and public domains) for mobile user deployments and
remote network sites.
- Set up internal domain lists that apply to all traffic.
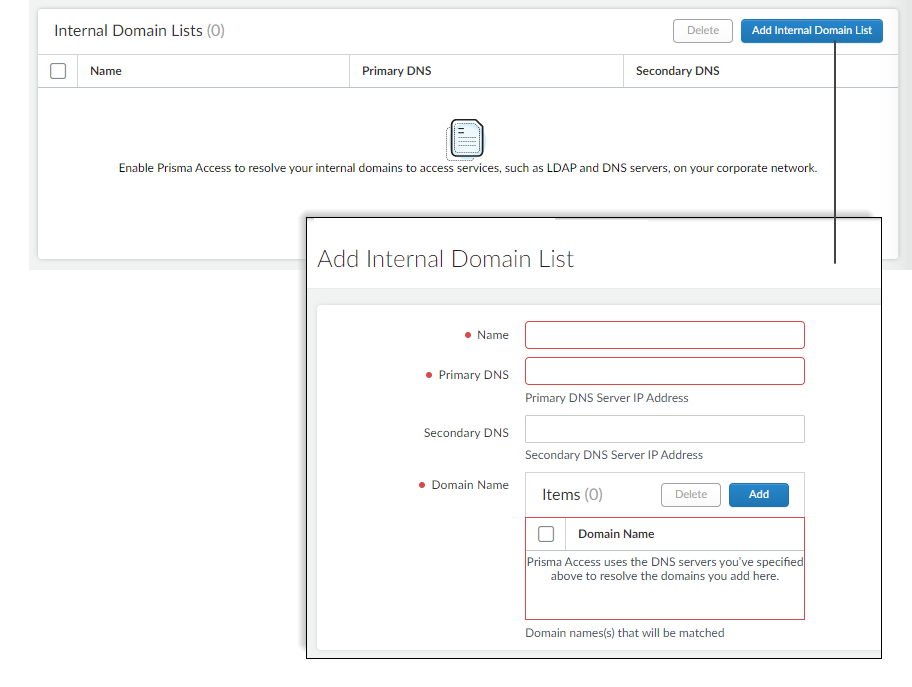
- Select ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessPrisma Access Infrastructure and Add Internal DNS Servers.
![]() Enter the primary DNS server and secondary DNS server that Prisma Access should use to resolve the internal domain names.Add the internal domain names to send to these DNS servers for resolution.You can use a wildcard (*) in front of the domains in the domain list, for example *.acme.local or *.acme.com.Add internal domain lists that apply only to specific mobile user deployments or remote network sites.
Enter the primary DNS server and secondary DNS server that Prisma Access should use to resolve the internal domain names.Add the internal domain names to send to these DNS servers for resolution.You can use a wildcard (*) in front of the domains in the domain list, for example *.acme.local or *.acme.com.Add internal domain lists that apply only to specific mobile user deployments or remote network sites.- Configure DNS settings:
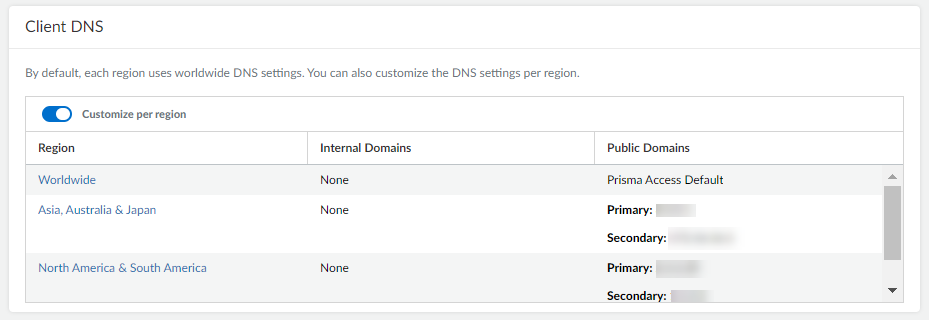
- Mobile Users—Go to ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessGlobalProtectInfrastructure Settings and find Client DNS.
![]()
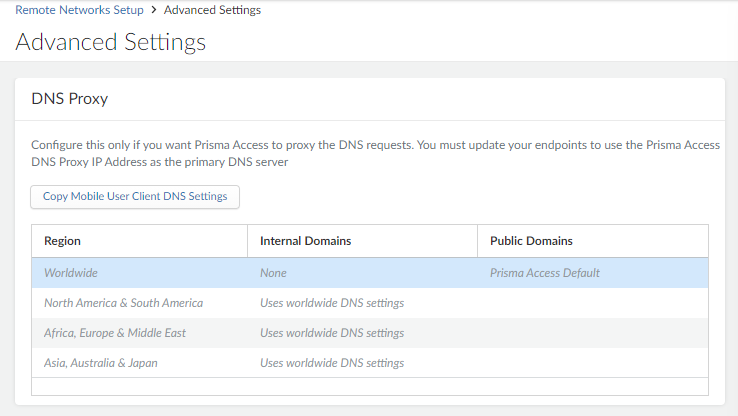
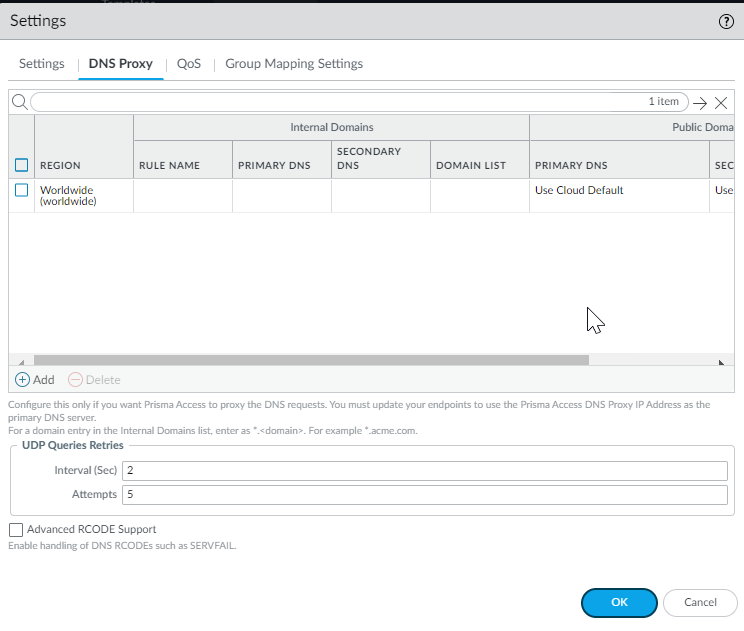
- Remote Networks—Go to ConfigurationNGFW and Prisma AccessConfiguration ScopePrisma AccessRemote NetworksAdvanced Settings and find DNS Proxy.
![]()
- Use the Worldwide default (the Prisma Access default DNS server) or customize settings based on region. In either case, select the region to adjust and customize the DNS settings for that region.
- Check the option to use these DNS settings to resolve internal domains and optionally Use the internal DNS Server for resolving public domains too. If you don’t select this option, Prisma Access uses its cloud default DNS server to resolve requests for public domains.
- Allow traffic from all addresses in your mobile user IP address pool to-your DNS servers.The DNS proxy in Prisma Access sends the requests to the DNS servers you specify. The source address in the DNS request is the first IP address in the IP pool you assign to the region. To ensure that your DNS requests can reach the servers you will need to make sure that you allow traffic from all addresses in your mobile user IP address pool to your DNS servers.
DNS for Prisma Access (Panorama)
Prisma Access allows you to specify DNS servers to resolve both domains that are internal to your organization and external domains.Set up Prisma Access to resolve internal domains. - Set up internal domain lists that apply to all traffic.
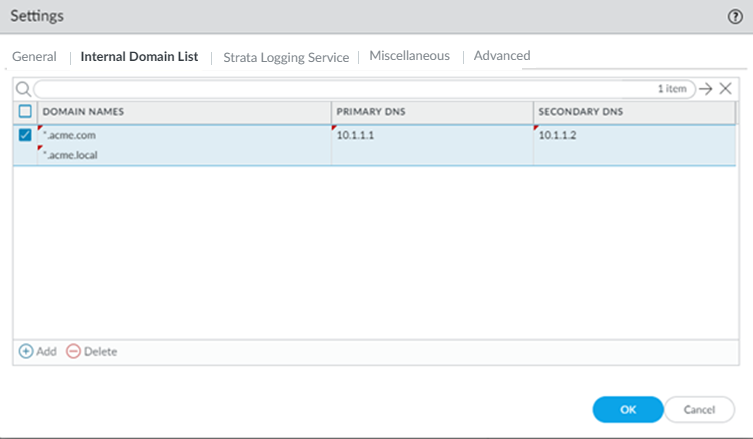
- Select PanoramaCloud ServicesConfigurationService Setup and click the gear icon to edit the Settings.Select the Internal Domain List tab.Add the Domain Names, Primary DNS, and Secondary DNS servers that you want Prisma Access to use to resolve your internal domain names.You can use a wildcard (*) in front of the domains in the domain list; for example *.acme.local or *.acme.com.
![]() Add internal domain lists that apply only to specific mobile user deployments or remote network sites.
Add internal domain lists that apply only to specific mobile user deployments or remote network sites.- Configure DNS settings:
- Mobile Users—Go to PanoramaCloud ServicesConfigurationMobile Users - GlobalProtect and select the external gateway and click Network Services.
![]()
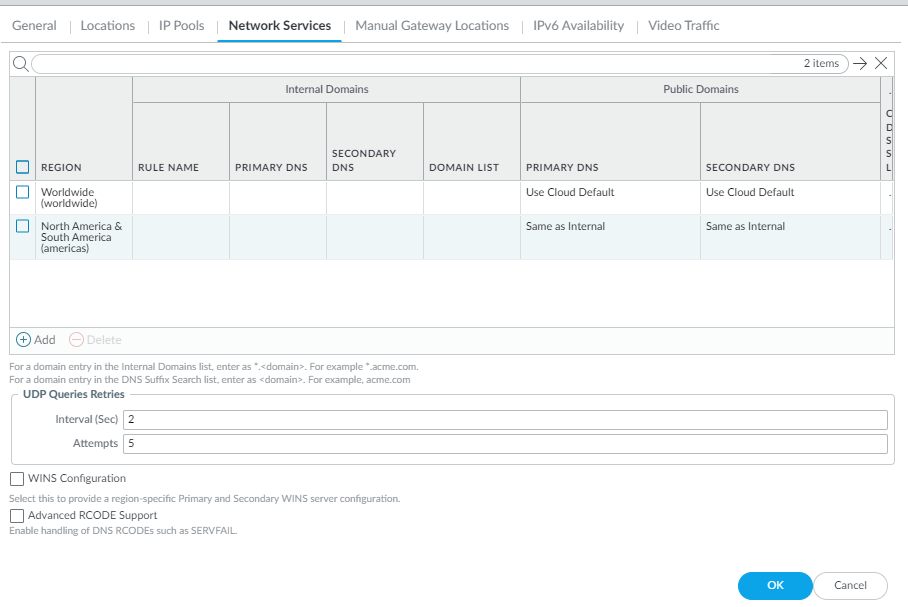
- Remote Networks—Go to PanoramaCloud ServicesConfigurationRemote Networks > Settings > DNS Proxy.
![]()
- Use the Worldwide default (the Prisma Access default DNS server) or customize settings based on region. In either case, select the region to adjust and customize the DNS settings for that region.
- Add one or more rules to configure the DNS settings for Internal Domain.
- Enter a unique Rule Name for the rule.
- You want your internal DNS server to only resolve the domains
you specify; enter the domains to resolve in the Domain List.
Specify an asterisk in front of the domain; for example,
*.acme.com. You can specify a maximum of 1,024 domain entries.
Prisma Access has a predefined rule to resolve *.amazonaws.com domains using the Cloud Default server. If you want your internal DNS servers to resolve a more-specific *.amazonaws.com domain (for example, *.s3.amazonaws.com), enter the URL in the Domain List. Prisma Access evaluates the domain names from longest to shortest, then from top to bottom in the list.
- If you have a Custom DNS server that can access your internal domains, specify the Primary DNS and Secondary DNS server IP addresses, or select Use Cloud Default to use the default Prisma Access DNS server.
- Specify the DNS settings for Public Domains.
- Use Cloud Default—Use the default Prisma Access DNS server.
- Same as Internal Domains—Use the same server that you use to resolve internal domains. When you select this option, the DNS Server used to resolve public domains is same as the server configured for the first rule in the Internal Domains section.
- Custom DNS server—If you have a DNS server that can access your public (external) domains, enter the Primary DNS server address in that field.
- (Optional) You can Add a DNS Suffix to specify the suffix that the client should use locally when an unqualified hostname is entered that it cannot resolve, for example, acme.local. Do Prisma Access Administrator’s Guide (Panorama Managed) not enter a wildcard (*) character in front of the domain suffix (for example, acme.com). You can add multiple suffixes.
- Allow traffic from all addresses in your mobile user IP address pool to-your DNS servers.The DNS proxy in Prisma Access sends the requests to the DNS servers you specify. The source address in the DNS request is the first IP address in the IP pool you assign to the region. To ensure that your DNS requests can reach the servers you will need to make sure that you allow traffic from all addresses in your mobile user IP address pool to your DNS servers.